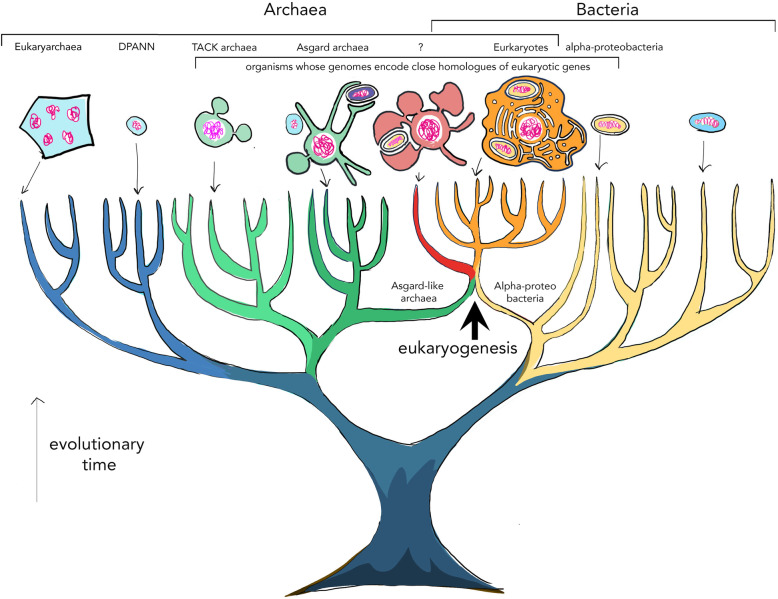
Fig. 1.
Tree of life: The tree summarizes the broadscale evolution of life on Earth. The two main branches depict the bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotes possess genes of both bacterial and archaeal ancestry and arose from the merger of a host cell, closely related to the Asgard superphylum of archaea, with a member of the alpha-proteobacteria, which gave rise to mitochondria. Drawings depict present-day examples of cells from different tips of the tree of life, emphasizing steps that likely connect the cell structures of TACK archaea, Asgard archaea, and eukaryotes. The question mark depicts a hypothetical intermediate along this path that is predicted by the inside-out model (3), whose living descendants we would hope might be identified in the coming years. This is an Asgard-type archaeon that forms intimate connections with its obligate symbiotic partner—an alpha-proteobacterium