Figure 2. Activation of group III mGluRs decreases the firing activity of spinally projecting PVN neurons in WKY rats but produced divergent effects in SHRs.
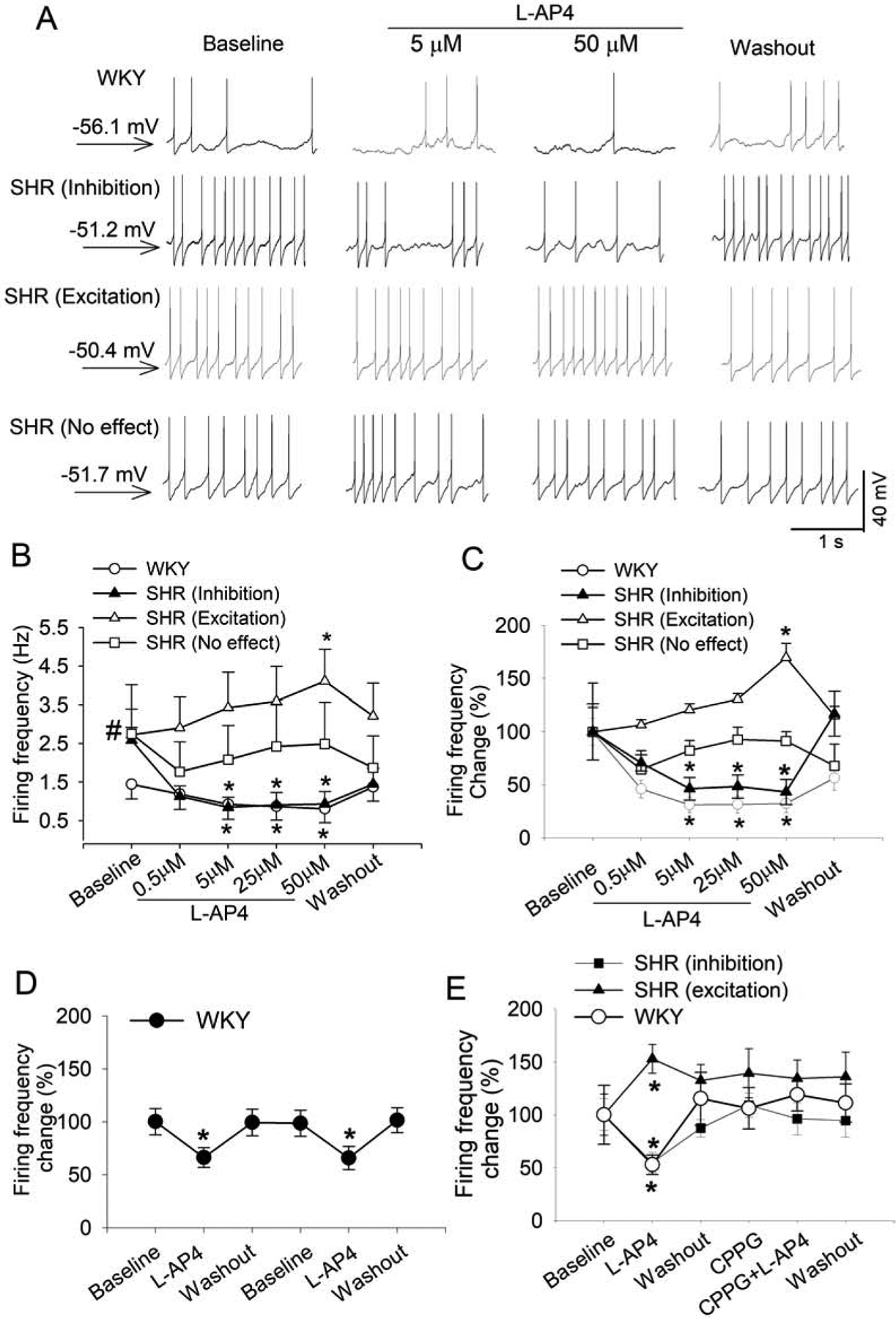
A, Original traces show the effect of L-AP4 on the firing activity of labeled PVN neurons in one WKY rat and one SHR. The membrane potential value was shown on the left. B and C, Mean data (B) and percentage changes (C) show the concentration-dependent effect of L-AP4 on the firing activity of labeled PVN neurons in WKY rats (n = 15 neurons from 4 rats) and SHRs (n = 22 neurons from 6 rats). The firing rate was normalized to the respective baseline in each group. D, Mean data show the effect of repeated bath application of 50 μM L-AP4 on the firing rate of 9 labeled PVN neurons from 4 rats in WKY rats. E, Summary data show that CPPG blocked the effect of L-AP4 on the firing rate of labeled PVN neurons in WKY rats (D, n = 9 neurons from 4 rats) and SHRs (E; inhibition, n = 10 neurons; excitation, n = 7 neurons from 5 rats). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, compared with the baseline for the group. #P < 0.05, compared with the baseline in WKY rats.
