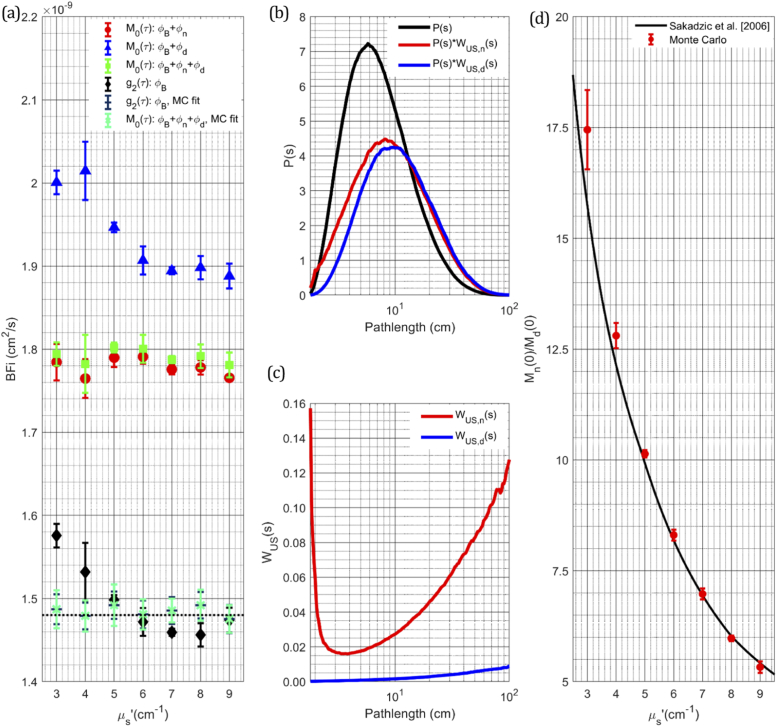
Fig. 2.
(a) Comparison of the BFi values extracted from the simulated intensity autocorrelations and their modulation depths, using the correlation diffusion equation for a range of reduced scattering that could be seen in vivo. (b) Pathlength distributions of the autocorrelation and modulation depths of individual mechanisms, the increased BFi measured from the modulation depth can be explained by the increased influence of longer pathlengths for both ultrasound mechanisms for modulation. (c) Comparison of the mean squared phase accumulation as a function of pathlength for both mechanisms of ultrasound modulation showing index of refraction modulation contributing to a larger degree than that of ultrasound scatterer displacement. (d) Comparison of the ratio of the modulation depth from each mechanism at zero lag compared to previously derived results as a function of scattering property.