Figure 2: The ATR/CHK1/WEE1 pathway compensates for the replicative stress induced by gemcitabine.
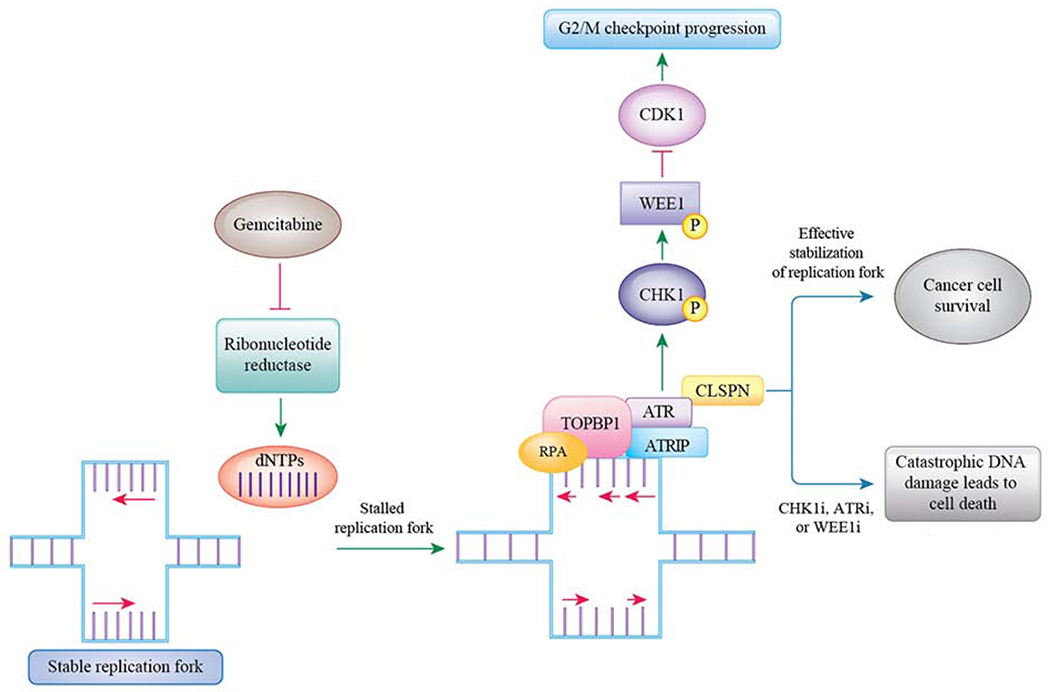
Gemcitabine causes replicative stress by irreversibly inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase and thereby decreasing dNTP concentration. Decreased dNTP concentration causes stalled replication forks. In response to this replicative stress, the ATR/CHK1/WEE1 pathway is activated and this leads to stabilization of the replicative forks. However, inhibitors of the ATR/CHK1/WEE1 pathway block this compensatory pathway. This leads to persistence of unstable replication forks and ultimately causes genomic catastrophe leading to cancer cell death.
