Figure 6. Hypothesized effect of empagliflozin on glycerol-derived hepatic gluconeogenesis.
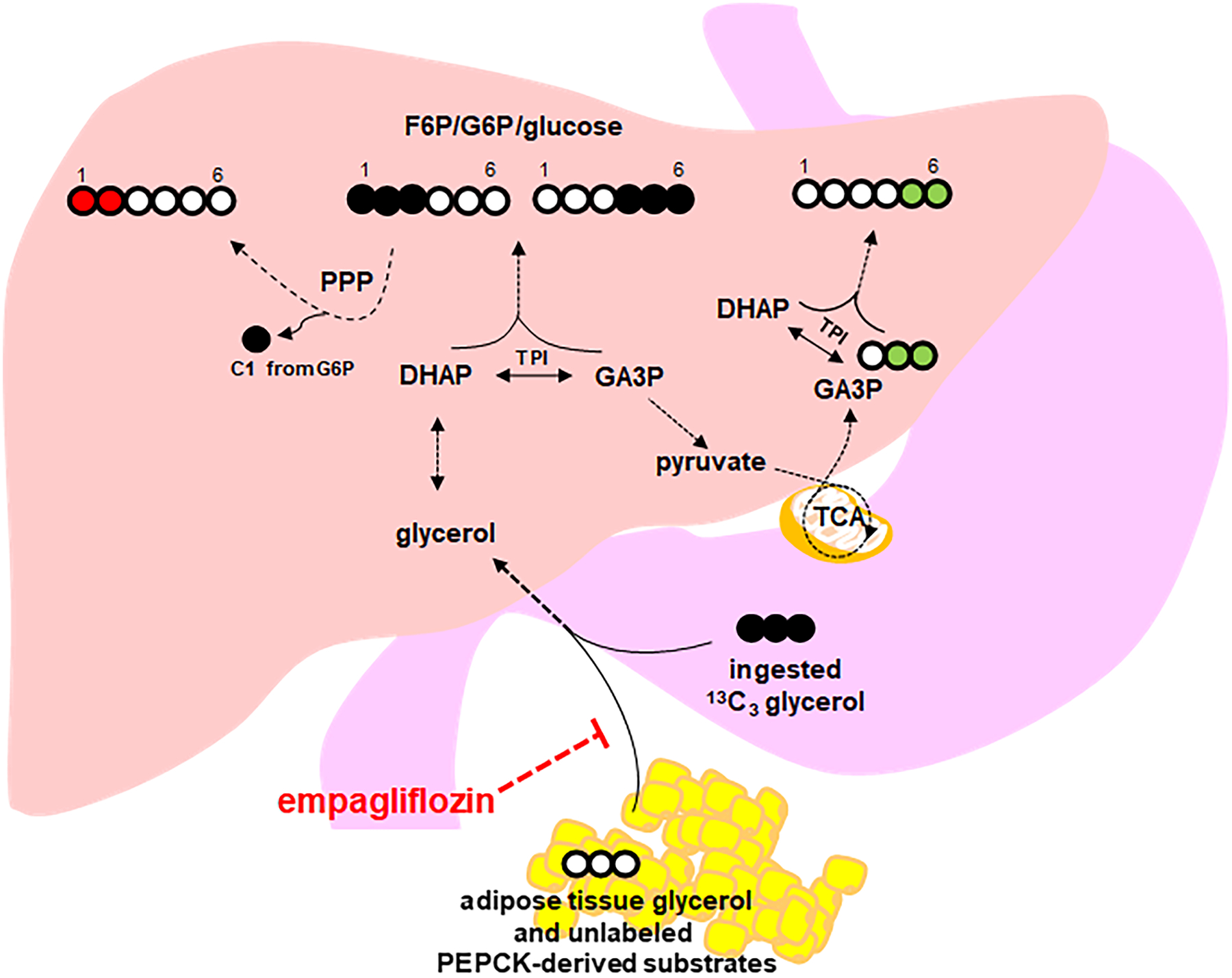
Glycerol-gluconeogenesis is directly interrogated by determining the fraction of 13C3 enrichment in blood glucose using NMR spectroscopic quantification of 13C–labeled glucose isotopomers. Total 13C enrichment in plasma glucose is measured by the sum of all glucose isotopomers with excess 13C. Empagliflozin treatment may decrease visceral adipose tissue thereby reducing its contribution of cold (endogenous) glycerol and/or cold PEPCK-derived substrates into this pathway (red hashed flat arrow). Additional information about specific pathways is derived from specific glucose isotopomers. Initially, glycerol is phosphorylated in the liver by glycerol kinase and is converted to DHAP and GA3P. Direct production of glucose via gluconeogenesis occurs by condensation of DHAP and GA3P to form carbons 1–3 and 4–6 of glucose, respectively. Therefore, quantification of [1,2,3-13C3] glucose and of [4,5,6-13C3] glucose reflects primarily direct hepatic gluconeogenesis from ingested [U-13C3] glycerol (black filled circles). Passage of [1,2,3-13C3] G6P through the PPP produces [1,2-13C2] F6P and subsequently [1,2-13C2] glucose so that the quantification of [1,2-13C2] glucose reflects PPP activity (red filled circles). Metabolism of [U-13C3] glycerol to [U-13C3] pyruvate followed by either decarboxylation to [U-13C2] acetyl-CoA or carboxylation to [1,2,3-13C3] oxaloacetate allows rearrangement of 13C in the TCA cycle to form PEP. Two possible PEP isotopomers through glycerol metabolism in the TCA cycle are [1,2-13C2]- and [2,3-13C2] PEP. Conversion to PEP and metabolism to glucose will produce [4,5-13C2]- or [5,6-13C2] glucose (green filled circles). Since the PPP does not disrupt carbon–carbon bonds in carbons 4–6 of glucose, the presence of [4,5-13C2]- or [5,6-13C2] glucose indicates metabolism of [U-13C3] glycerol through the TCA cycle prior to gluconeogenesis. DHAP = dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GA3P = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; G6P = glucose 6-phosphate; F6P = fructose 6-phosphate; NMR = nuclear magnetic resonance; PEP = phosphoenolpyruvate; PEPCK = PEP carboxykinase; PPP = pentose phosphate pathway, TCA = tricarboxylic acid; TPI = triose phosphate isomerase.
