Figure 3.
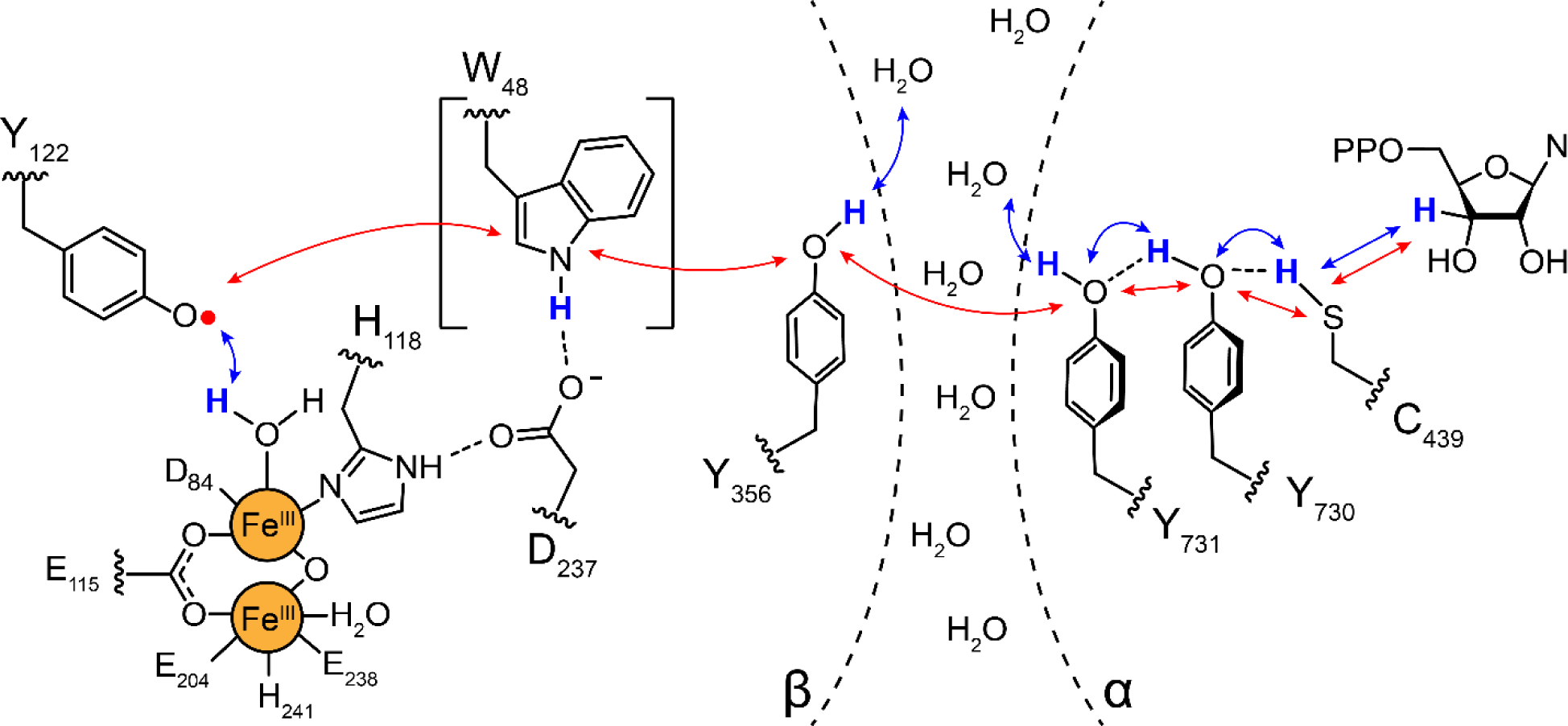
Proposed radical transfer pathway in Ia RNRs (E. coli numbering) within the α2β2 complex. Binding of substrate and allosteric effector (not shown) to α2, triggers radical transfer from the Y122• of the Fe3+2-Y122• cofactor in β, through three transient Y•s (356-β across the subunit interface to 731-α and 730-α). The Y730•- α (under the gray circle in Figure 1B) then oxidizes the active site cysteine to a −S• that initiates NDP reduction (Figure 1A). Subsequent to dNDP formation, the Y122• is regenerated by reverse radical transfer. W48-β is bracketed as its role in the pathway has not been established. Each step in the pathway is proposed to involve distinct proton (H+, blue arrows) coupled electron (e−, red arrows) transfer (PCET) steps indicated by blue and red arrows (7).
