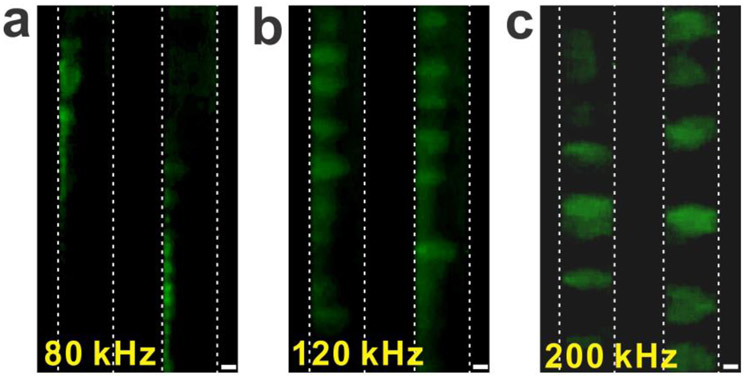
Figure 5.
Frequency dependent DEP and the DNA trapping pattern. (a) The low-frequency AC voltage generates strong pDEP, attracting DNA to the electrode (9 V, 80 kHz). (b) After increasing the frequency of the AC voltage (9 V, 120 kHz), DNA experiences slightly reduced pDEP, which causes the trapped DNA to partially move off from the electrode. (c) After further increasing the frequency of the AC voltage (9 V, 200 kHz), the DNA were fully stretched between the electrodes, indicating a significant dependence of the DEP strength and the DNA polarizability on the frequency of the applied AC voltage. The scale bar is 10 μm.