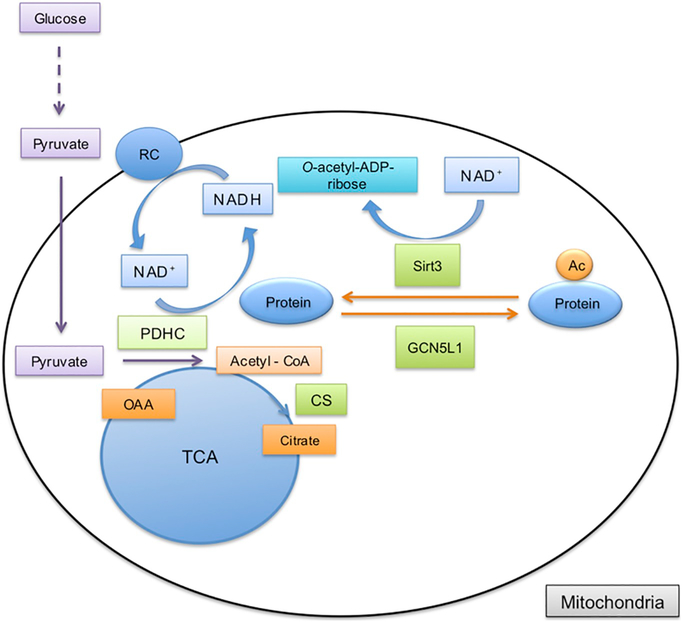
Fig. 2.
Mitochondrial acetyl-CoA metabolism and protein acetylation. Pyruvate formed during glucose metabolism in the cytosol is transported into the mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA is then generated by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC) from pyruvate. During this reaction NAD+ is reduced to NADH that donates electrons to complex I in the respiratory chain (RC). In the TCA cycle citrate is produced by citrate synthase (CS) from acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate (OAA). Acetyl-CoA can also be used by mitochondrial acetyltransferase, GCN5L1, to acetylate mitochondrial proteins. The acetyl group is removed from the target protein by mitochondrial deacetylase, Sirt3, which uses NAD+ and releases the deacetylated protein and o-acetyl-ADP-ribose.