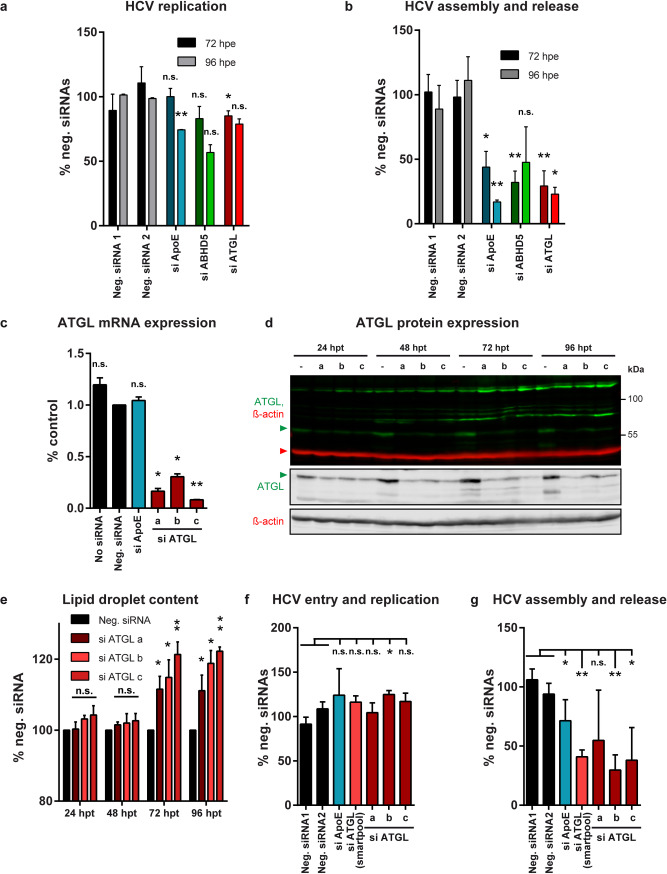
Fig 5. ATGL knockdown induces lipid droplet accumulation and reduces HCV assembly.
(a, b) Effect of pools of 3 siRNAs targeting ApoE or ABHD5 or 4 siRNAs targeting ATGL (SMARTpool) on HCV replication cycle (n = 3 for 72 hours post-electroporation (h.p.e.) and n = 2 for 96 h.p.e.). Lunet N hCD81 FLuc cells were electroporated with HCV RNA and transfected 4 hours later with the siRNA pools. Panel a represents the effects on the early replication events (RLUs in the producer cells). Panel b depicts the effects on HCV production (RLUs in the target cells normalized by RLUs in the producer cells). For the statistics, we compared the results obtained with the different siRNAs to the average of the negative siRNAs 1 and 2. (c-g) Effect of single siRNAs targeting ATGL (si ATGL a, b and c) on ATGL expression, lipid droplet content and HCV replication cycle. (c) ATGL mRNA expression was assessed 96 hours (h) post-transfection by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH (n = 2). (d) ATGL protein expression was verified by Western blot. The green and red arrowheads point at the ATGL and β-actin protein bands. (e) The lipid droplet content of cells transfected with ATGL-specific or control siRNAs was evaluated by flow cytometry at 24-48-72-96 hours post-siRNA transfection. (f, g) HCV JcR2a whole replication cycle was examined in the siRNA-transfected cells. (f) Entry and replication correspond to the RLuc reading in the producer cells at 48 h.p.i. normalized for the FLuc readings at the same time point, which reflect the cell viability and proliferation (n = 3, except SMARTpool where n = 2). (g) Assembly and release values are obtained by normalizing the RLuc readings in the target cells (infected with the 96 h.p.e. supernatants) by the RLuc readings in the producer cells at 48 h.p.e. (n = 4, except SMARTpool where n = 3).