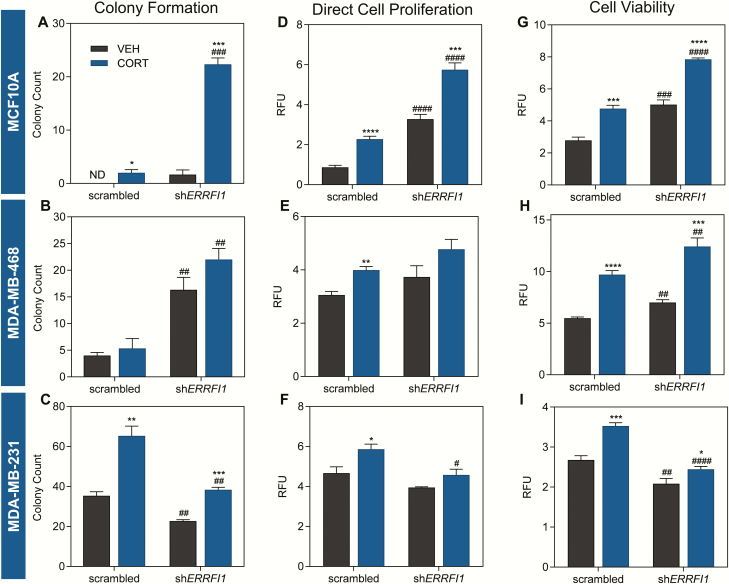
Figure 4.
ERRFI1 knockdown has different effects on cell survival, proliferation, and viability in TNBC. Effects of ERRFI1 knockdown and CORT treatment on (A-C) cell survival, (D-F) direct cell proliferation, and (G-I) cell viability of TNBC cells were evaluated using assays based on colony formation, fluorescence-based DNA-binding, and resazurin reduction, respectively. For the colony formation assay, scrambled and shERRFI1 cells were treated with vehicle (100% ethanol) or CORT (100 nM) for 14 days. For the direct cell proliferation and cell viability assay, cells were treated as previously described for 72 h. In MCF10A, CORT (A) enhanced colony formation (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,8) = 201.0, P < 0.0001; Knockdown factor: F(1,8) = 189.4, P < 0.0001), (D) increased cell proliferation (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,15) = 110.2, P < 0.0001; Knockdown factor: F(1,15) = 239.3, P < 0.0001), and (G) increased cell viability (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,14) = 97.85, P < 0.0001; Knockdown factor: F(1,14) = 118.2, P < 0.0001). These effects of CORT were enhanced by ERRFI1 knockdown. CORT treatment of MDA-MB-468 cells (B) did not affect cell survival (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,8) = 3.615, P = 0.0938; Knockdown factor, F(1,8) = 62.04, P < 0.0001), (E) slightly augmented cell proliferation (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,12) = 13.38, P = 0.0033; Knockdown factor: F(1,12) = 6.215, P = 0.0283), (H) and increased cell viability (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,14) = 158.3, P < 0.0001; Knockdown factor: F(1,14) = 28.99, P < 0.0001). Knockdown of ERRFI1 increased cell survival and viability independent of the pro-tumorigenic effects of CORT but had no effect on cell proliferation. In MDA-MB-231, CORT treatment (C) promoted colony formation (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,8) = 71.64, P < 0.0001; Knockdown factor: F(1,8) = 54.05, P < 0.0001), (F) enhanced proliferation (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,13) = 13.56, P = 0.0028; Knockdown factor: F(1,13) = 16.52, P = 0.0013), and (I) increased viability (2-way ANOVA; Treatment factor: F(1,16) = 31.27, P < 0.0001; Knockdown factor: F(1,16) = 61.37, P < 0.0001). Knockdown of ERRFI1 conferred anti-tumorigenic effect in the cell line. For the cell proliferation and cell viability assays, measures were normalized to raw fluorescence reads at 0 h, which was set as baseline (relative fluorescence units), and normalized values were log10 transformed before statistical analysis. Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean with statistical significance determined through Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 for statistically significant effects of CORT within a shRNA type, and #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 for statistically significant effects of ERRFI1 knockdown between the same hormone treatment). For the colony formation assay, treatments were performed with 3 replicates, while for the direct cell proliferation and cell viability assays, treatments were done with 5 replicates. All experiments were performed at least twice with consistent results and graphs shown are representative of the different trials.