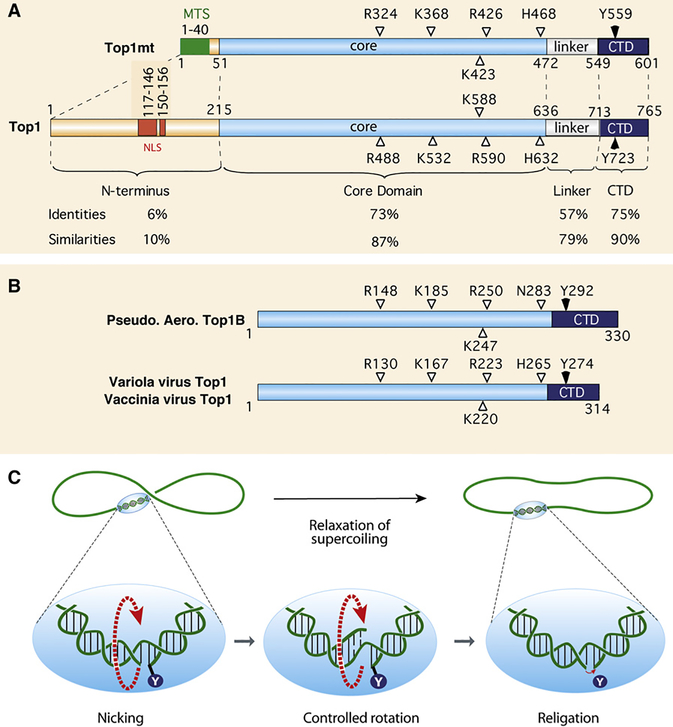
Figure 2. Overview of Type IB Topoisomerases and Relaxation by Nicking-Closing Activity.
(A) Schematic representation of the two human type IB enzymes. Top1mt has a much shorter N-terminal segment consisting primarily of a mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) and lacking the nuclear localization sequences (NLS) of Top1 (nuclear). The catalytic homologous residues are indicated with their position.
(B) Schematic representation of the poxvirus (variola and vaccinia) Top1s and comparison with the recently discovered bacterial Top1B (Pseudomonas aeroginosa).
(C) Top1-mediated DNA relaxation by controlled rotation. By contrast to type IA or II enzymes, this reaction does not require an energy cofactor or divalent metal. Top1 tends to bind DNA crossovers (supercoils) and nicks DNA by transesterification (see Figure 1D). The enzyme then allows the DNA to swivel by controlled rotation (Koster et al., 2005; Stivers et al., 1997). Upon DNA realignment by base pairing and stacking across the nick, the DNA 5′-hydroxyl end (OH in lower panels) removes the tyrosyl linkage by reverse transesterification (see Figure 1D).