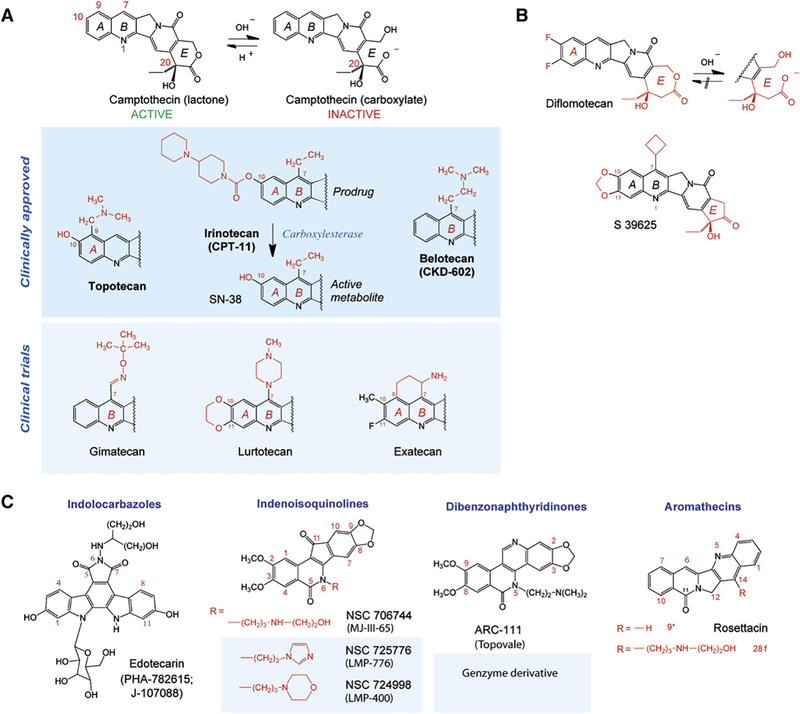
Figure 3. Top1 Inhibitors.
(A) Camptothecin and its clinical derivatives. The facile and reversible opening of the α-hydroxylactone E ring of camptothecin is shown at the top. Topotecan and irinotecan are the two FDA-approved camptothecins. Irinotecan is a prodrug; its active metabolite is SN-38. Belotecan is approved in South Korea.
(B) Synthetic E-ring-modified camptothecin derivatives. Whereas diflomotecan (a homocamptothecin) can still be converted irreversibly to a carboxylate, the α-keto derivative S39625 is chemically stable while still being a potent Top1 inhibitor.
(C) Noncamptothecins. The indenoisoquinolines and one dibenzonaphthyridinone are beginning clinical trials.