Fig. 3. GFP-VBP dimerization and DNA binding mutants by FRAP.
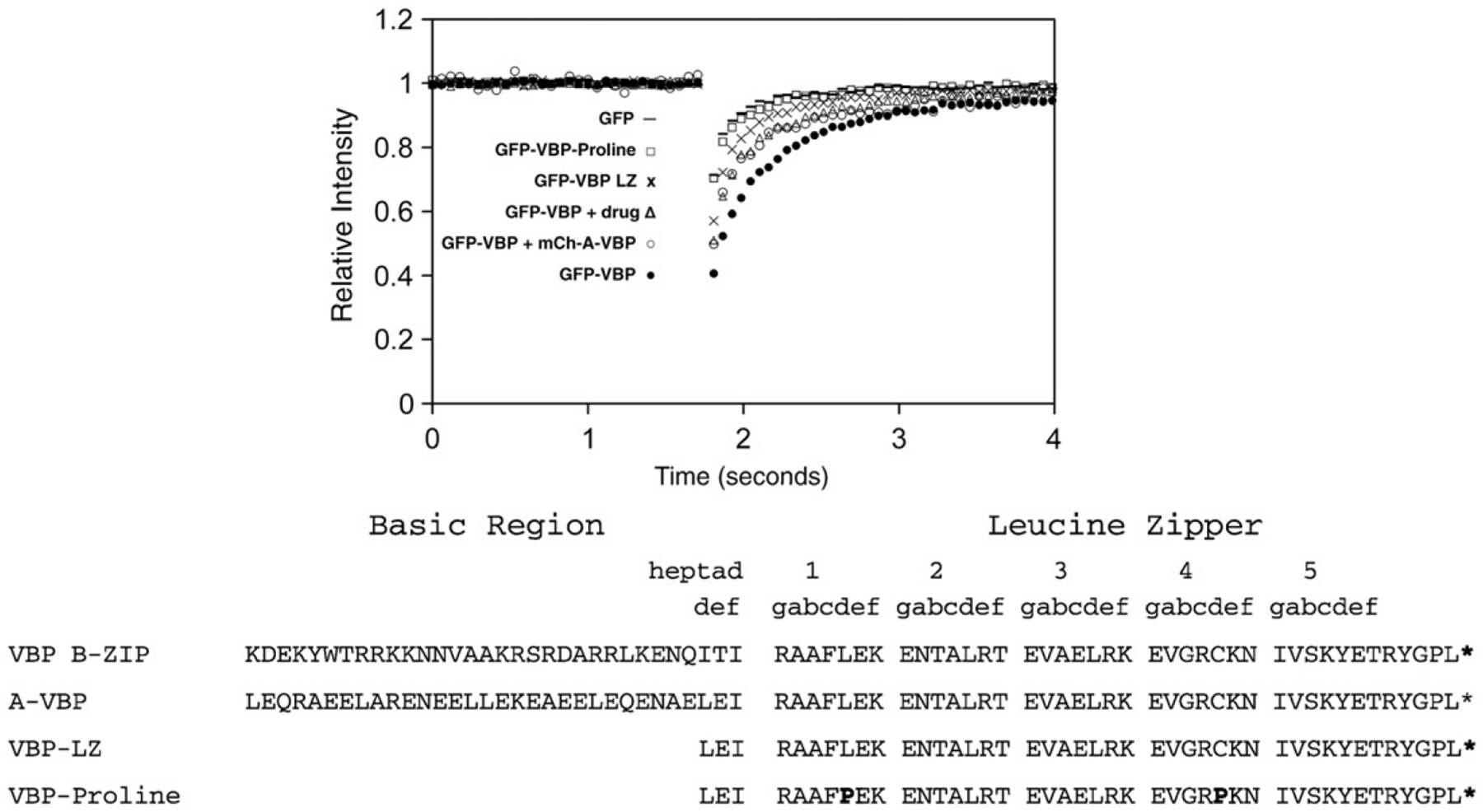
NIH3T3 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids containing mutations in the GFP-VBP B-ZIP domain and analyzed by FRAP as previously described. GFP-VBP (●) containing the basic region and leucine zipper region has the slowest recovery. Inhibition of VBP DNA binding by incubation with 100 μM NSC13746 (Δ) or co-transfection of GFP-VBP with mCherry-A-VBP (○) cause an increase in GFP-VBP recovery. Deletion of the basic region of VBP (GFP-VBP-LZ (x)) causes faster GFP-VBP recovery. The recovery of monomeric GFP-VBP-Proline (☐) is faster than all GFP-VBP dimers, but is slower than monomeric GFP.
