Fig. 7. Inhibition of B-ZIP DNA binding by NSC13746 or A-ZIP causes B-ZIP cytoplasmic localization.
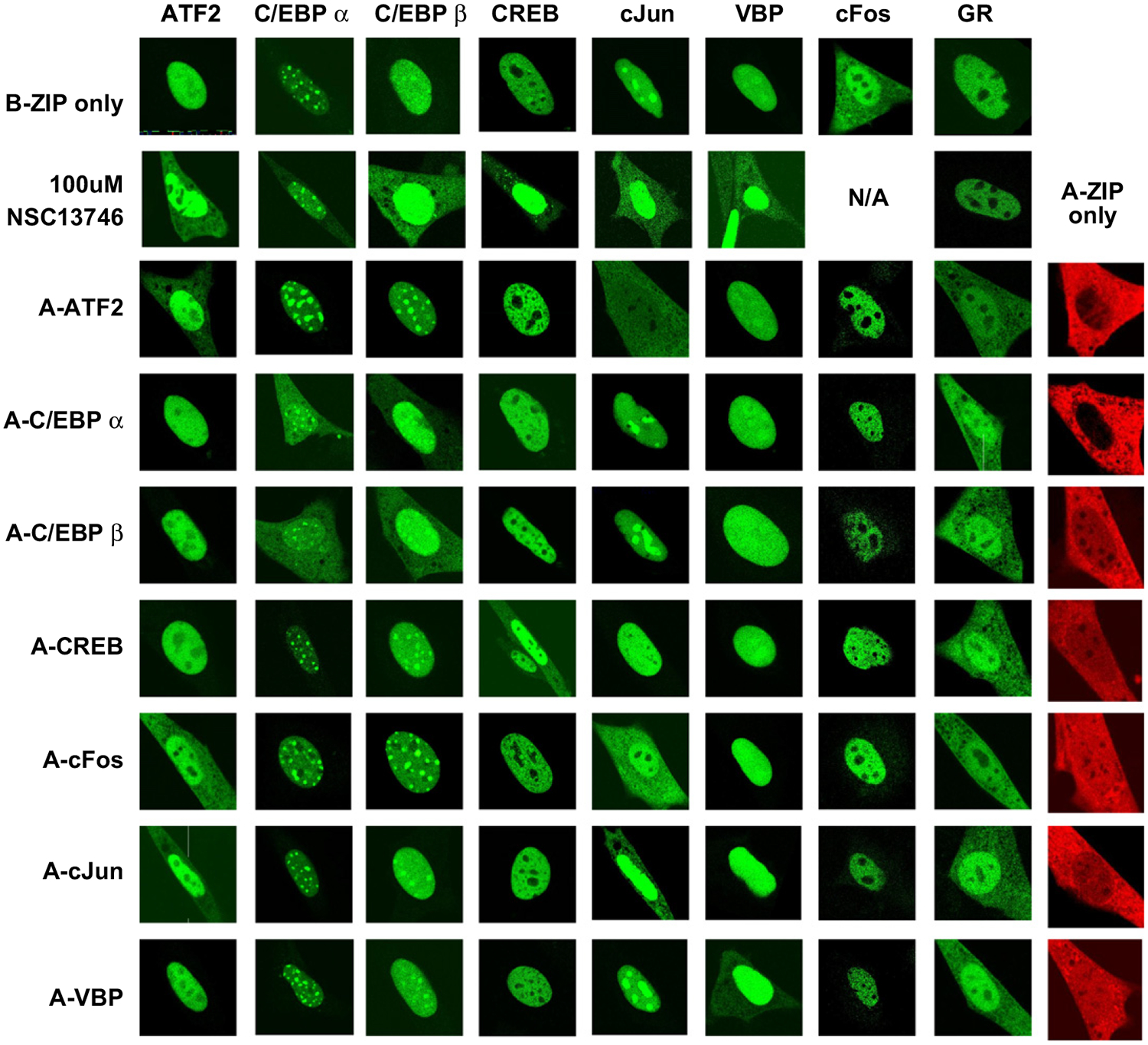
Cellular transfections were performed as described previously. Images were taken using a Zeiss 510 confocal microscope and are representative of at least 3 independent experiments in which at least 10–15 different cells were imaged in each experimental condition. GFP-B-ZIP domains localize to the nucleus, with the exception of cFos which does not homodimerize. mCherry-A-ZIPs (in red) are localized throughout the cell. Incubating GFP-B-ZIPs with100 μM of NSC13746 caused a cytoplasmic localization for all B-ZIPs. A matrix of GFP-B-ZIP and mCherry-A-ZIP co-transfections show an A-ZIP-dependent cytoplasmic localization of the B-ZIP partner.
