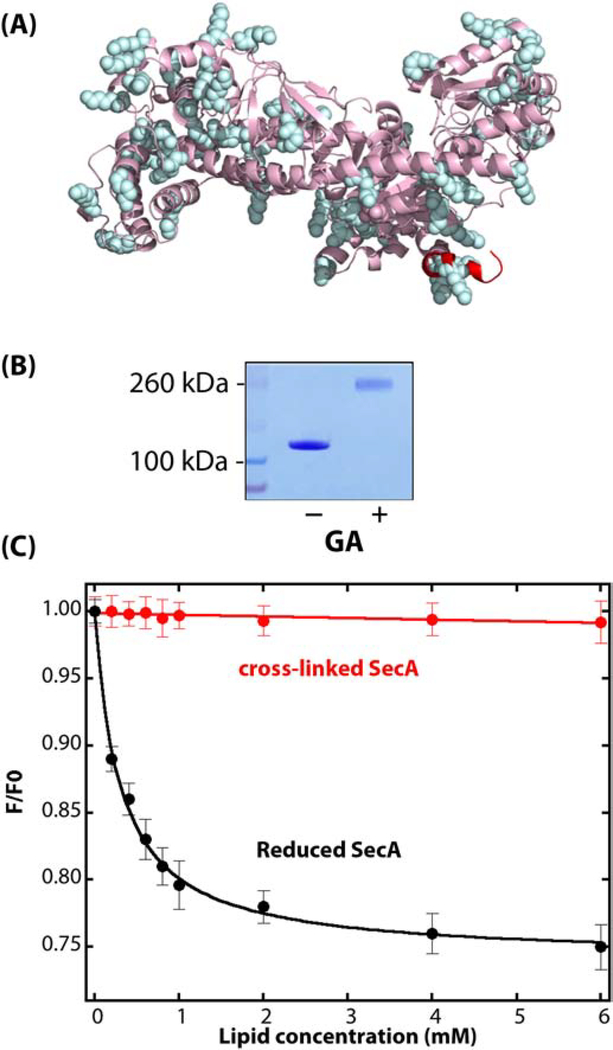
Figure 2.
Non-specific cross-linking of WT-SecA using glutaraldehyde (GA). (A) Side view of monomeric Escherichia coli SecA (PDB: 2FSF) with the membrane-partitioning N-terminus colored in red and lysine residues that are potential glutaraldehyde cross-linking sites highlighted in cyan. (B) Coomassie-blue stained SDS-PAGE gel of SecA protein (1 μM) in solution in the absence or presence of 0.15% GA. SecA in solution in the absence of vesicles was exposed to GA for 15 secs before halting the reaction with Tris-HCl. (C) GA-crosslinked SecA dimers do not partition significantly into E. coli LUV. The black curve shows the partitioning of untreated SecA (data from [49]). Titration of GA-crosslinked SecA (1 μM; 0.15% GA for 15 seconds) with LUV monitored by the change in intrinsic fluorescence is shown by the red curve. F0 is the fluorescence intensity at 340 nm in the absence of lipids, and F is the intensity in the presence of vesicles.