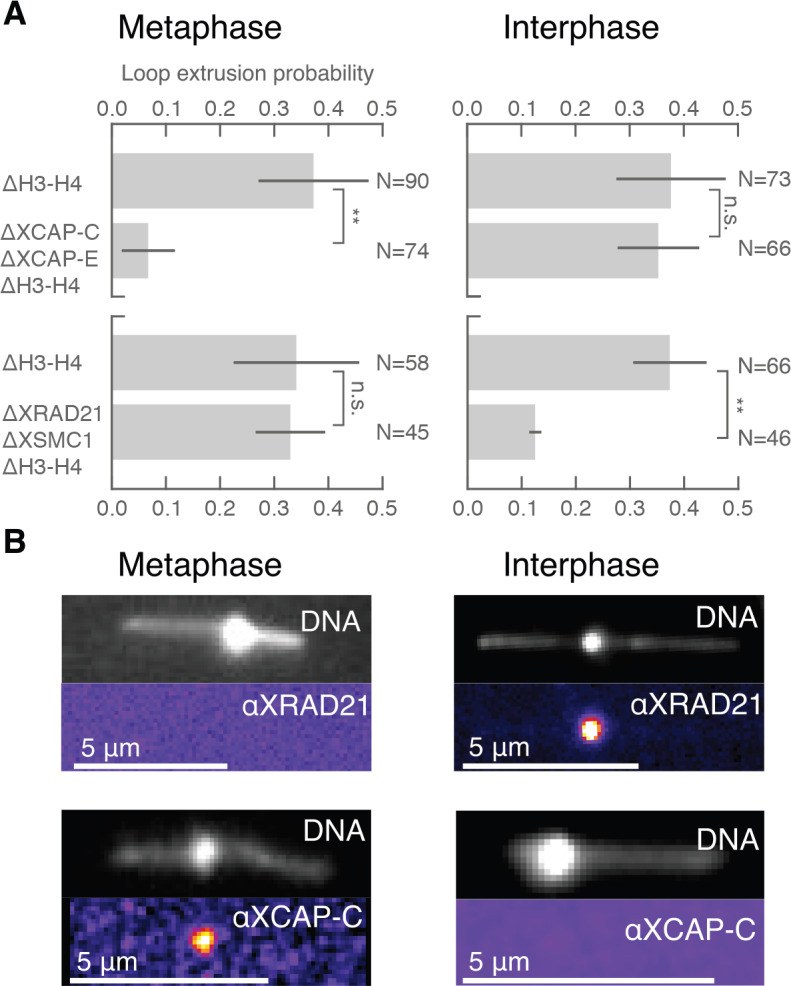
Figure 3. Condensin extrudes DNA loops in metaphase and cohesin extrudes loops in interphase.
(A) DNA loop extrusion probability—the frequency at which looping occurs on a DNA strand with sufficient slack—in metaphase and interphase under different depletion conditions. In metaphase, co-depleting condensin I, condensin II, and H3-H4 (using anti-XCAP-C/E and anti-H4K12Ac) significantly (** represents p<0.01, Binomial test) reduced loop extrusion probability, whereas the same depletion condition in interphase had no effect on loop extrusion probability compared to the control H3-H4-depleted extract. However, co-depleting cohesin and H3-H4 (using anti-XRAD21/XSMC1 and anti-H4K12Ac) had no effect in metaphase, though significantly (p<0.01) decreased loop extrusion probability in interphase compared to H3-H4-depleted extract. (B) Snapshots of antibody stainings of representative loops in metaphase and interphase. (Top) In metaphase, Alexa488-labeled anti-XRad21 bound to cohesin does not localize to the DNA loop, whereas in interphase (right panels), the anti-XRad21 co-localizes to the loop. (Bottom) Alexa488-labeled anti-XCAP-C bound to condensin localizes to the DNA loop in metaphase, but does not localize to the loop in interphase.