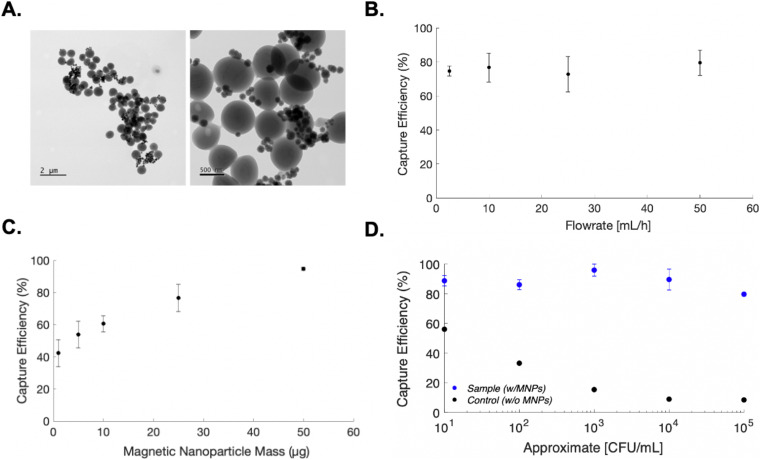
FIG. 3.
Microfluidic immunomagnetic bacterial capture. (a) Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) images of S. aureus bound to 150 nm magnetic nanoparticles. (b) Bacterial capture efficiency as a function of flow rate. (c) Bacterial capture efficiency as a function of magnetic nanoparticle mass. (d) Bacterial capture efficiency as a function of cell concentration. Control samples contained no functionalized magnetic particles and were evaluated to account for any potential bacterial loss and/or gain within the micro-system. All samples were evaluated in triplicate. Standard error of mean is reported.