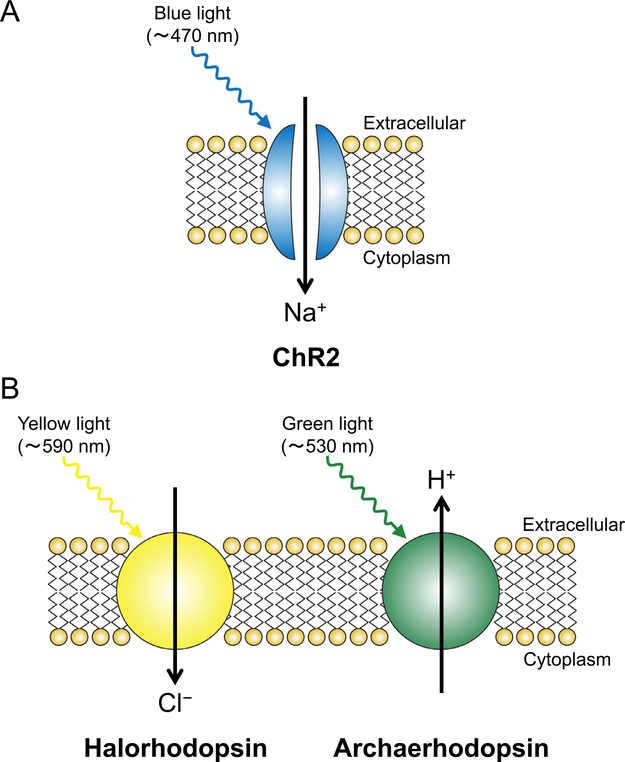
Figure 4.
Schematics of an (A) excitatory light-sensitive opsin, ChR2, and (B) inhibitory light-sensitive opsins, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin. The expression of these opsins does not affect the resting membrane potential because of the lack of ion flux without light application. (A) When ChR2 is illuminated with blue light, the gate of this nonselective cation channel is opened, which allows influx of Na+ and causes depolarization of the ChR2-expressing neurons. If the spike of Na+ entry is large enough for the membrane potential to reach the threshold, an action potential is evoked. (B) When halorhodopsin/archaerhodopsin is illuminated with yellow/green light, it functions as an inward Cl-/outward H+ pump and causes hyperpolarization of the neurons expressing these opsins, thereby exerting an inhibitory effect.