Figure 1. Results from multilevel growth modeling of longitudinal change in depressive severity across 10 years of adolescence.
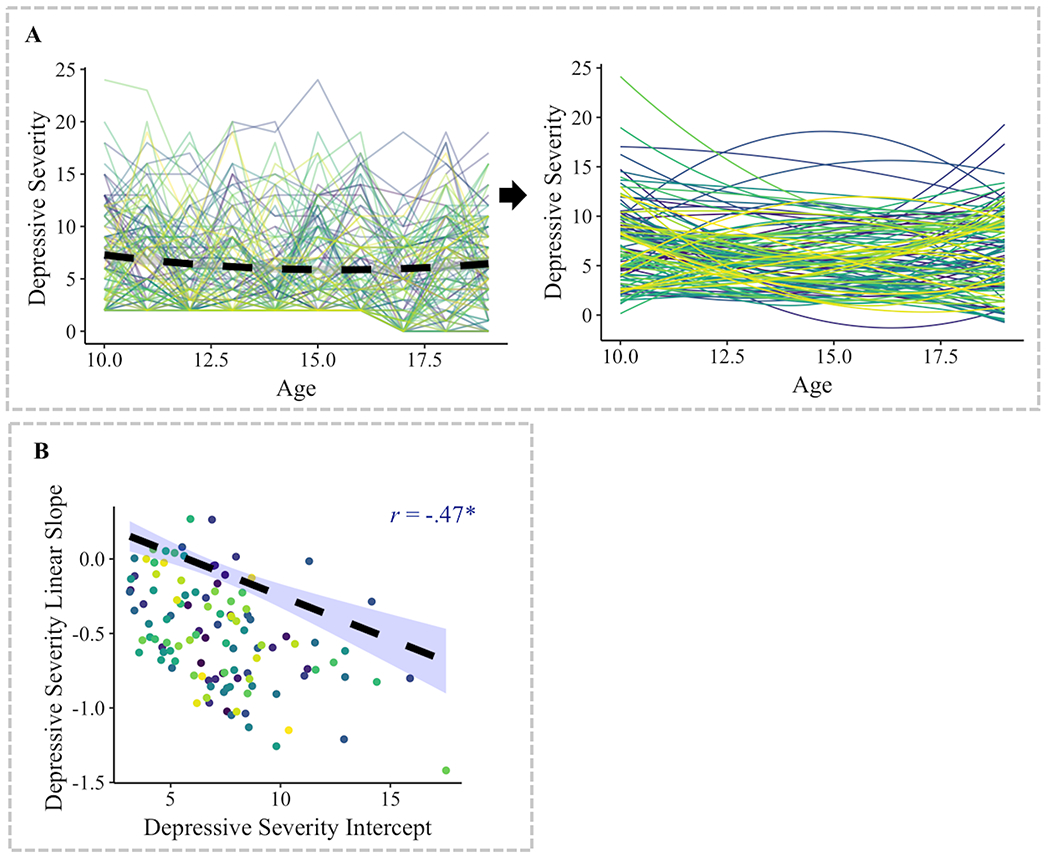
(A) A longitudinal multilevel quadratic model of change (with a fixed effect of the quadratic term) was fit to the data. Intercepts and linear slopes were estimated per individual. Individuals significantly varied in depressive intercept, linear slope, and the association between these variables. (B) There was a significant negative correlation between the initial status (i.e., intercept) and linear slope of depressive severity.
