Figure 2. RSV infection increases Uric acid production in the airways.
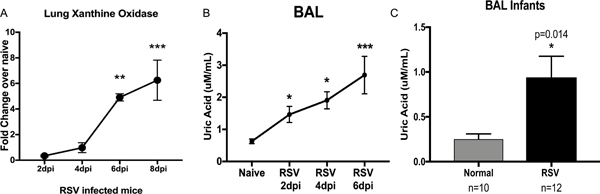
A) qPCR of Xanthine Oxidase (XO) in the lung of RSV infected mice shows significantly increased expression of XO during infection. B) The uric acid levels in bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) of RSV infected mice were significantly increased in the BAL of infected mice compared with the uric acid level in naive mice. Data represents the Mean ± SE from 4–5 mice (experimental repeats 3–4). * P≤0.05, ** P≤.01, *** P≤0.001. C) Uric acid levels from samples of lung aspirates from RSV+ and normal infants, with significant upregulation in RSV+ infants. * P≤0.05, ** P≤.01.
