Figure 6. Targeting the xanthine/uric acid pathway during RSV infection attenuates the immunopathology response.
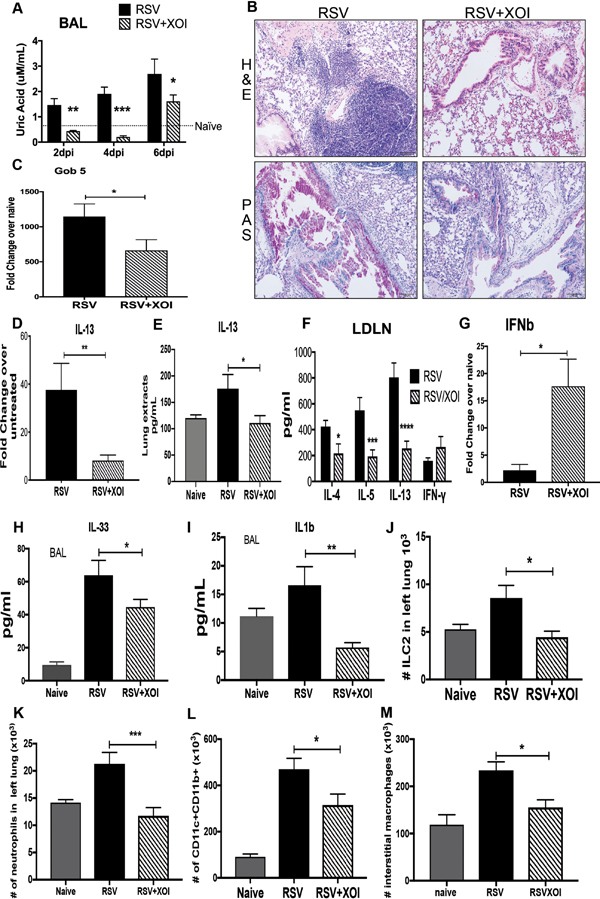
A) Uric acid detection in the BAL of infected mice was significantly decreased in mice treated with XOI compared with control and RSV infected mice. B) Lung histopathology in Hematoxylin and Eosin stain (H&E) showed inflammatory infiltrates and Periodic acid-Schiff stain (PAS) to detected mucus that was reduced in the lungs of mice treated with XOI, as well as C) decreased Gob 5 mRNA expression. D and E) IL-13 lung mRNA expression and production in lung extracts. F) Lung draining lymph nodes from mice at 8 were re-stimulated with RSV (MOI of 1, 48 hrs.), and T-cell cytokine levels were measured by Bio-Plex. G) qPCR of total lung RNA IFNβ mRNA expression. H and I) ELISA of IL-33 and IL-1β from BAL samples collected at 6dpi. J-M) Flow cytometry of lung leukocytes, ILC2, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and interstitial macrophages from naïve and infected mice at 8dpi. Data represents the Mean ± SE from 4–5 mice (experimental repeats 4–5). * P≤0.05, ** P≤.01, *** P≤0.001
