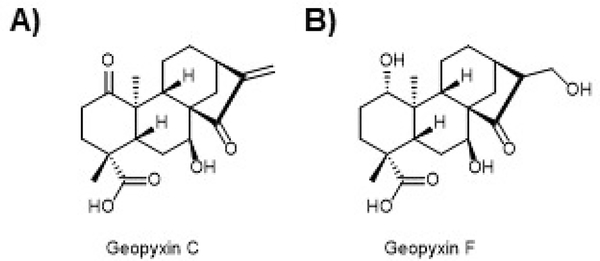
Figure 12. The geopyxins offer insight into the advantages of non-covalent NRF2 activation.
A) A series of ent-kaurane diterpenoids were shown to activate NRF2. Geopyxin C from Geopyxis aff. majalis, a fungus occurring in the lichen Pseudevernia intensa, was shown to potently activate NRF2 in a KEAP1-Cys151 manner. B) Geopyxin F from Geopyxis sp. AZ0066 inhabiting the lichen Pseudevernia intensa was shown to be a modest activator of the NRF2 pathway. However, geopyxin F was shown to activate NRF2 in a KEAP1-dependent, but Cys151-independent manner. Moreover, geopyxin F showed greater protection of cells against toxicants and that this protection was NRF2-dependent.