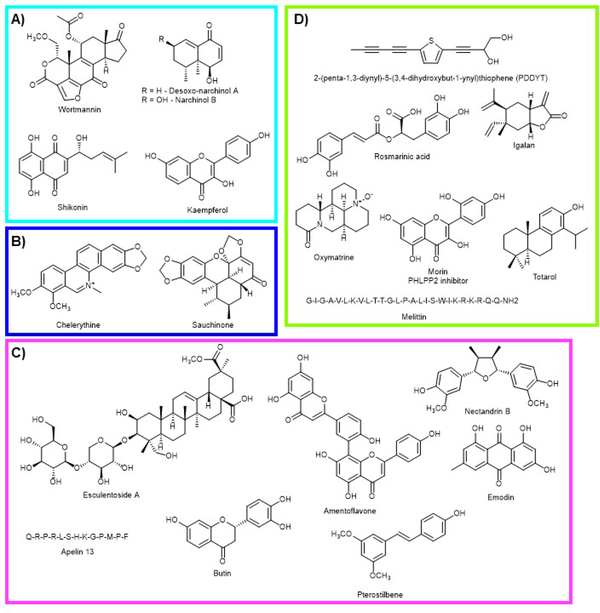
Figure 14. NRF2 modulating compounds that modulate the GSK-3β/NRF2/β-TrCP regulatory axis.
A) PI3K inhibitors that inhibit NRF2 by blocking PI3K. Wortmannin from Penicillium funiculosum. Despxo-narchinol A and narchinol B from Nardostachys jatamansi. Shikonin from Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Kaempferol from Brassica oleracea var. viridis. B) PKC modulators. Chelerythrine (Chelidonium majus) inhibits PKC and sauchinone (Saururus chinensis) activates PKC leading to inhibition of NRF2 and activation of NRF2, respectively. C) Compounds that activate AKT/PKB by increasing the activity of AMPK. Nectandrin B from Myristica fragrans. Emodin from Rheum hybridum. Esculentoside A from Phytolacca esculenta. Amentoflavone from Ginkgo biloba. Butin from Vernonia anthelmintica. Pterostilbene from blueberries. Apelin 13 from humans. D) Miscellaneous compounds that activate AKT/PKB by unknown mechanisms or through routes described in the text. 2-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-5-(3,4-dihydroxybut-1-ynyl)thiophene (PDDYT) from Echinops grijsii. Rosmarinic acid from Rosmarinus officinalis. Igalan from Inula helenium L. Oxymatrine from Sophora flavescens. Morin from Maclura pomifera. Totarol from Podocarpus totara. Melittin from honeybee (Apis mellifera) venom.