Figure 2.
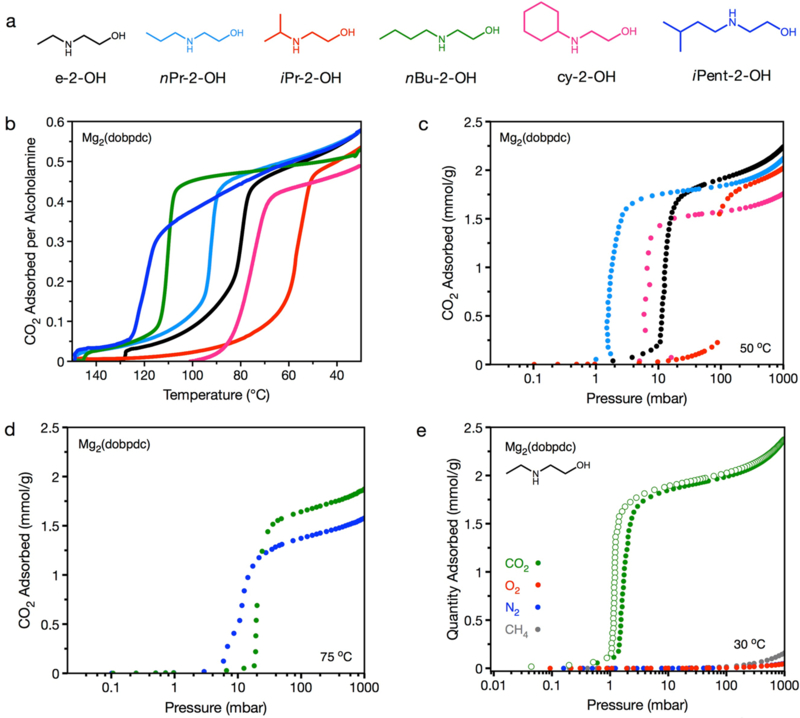
(a) Structures of e-2-OH–, nPr-2-OH–, iPr-2-OH–, nBu-2-OH–, cy-2-OH–, and iPent-2-OH alcoholamines appended to Mg2(dobpdc). Colors correspond to data presented in plots in (b)–(d) for the respective alcoholamine-appended frameworks. (b) Pure CO2 adsorption isobars obtained at 1 bar for e-2-OH–, nPr-2-OH–, iPr-2-OH–, nBu-2-OH–, cy-2-OH–, and iPent-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc), as measured by thermogravimetric analysis. Each framework exhibits a maximum capacity of 1 CO2 molecule per two alcoholamines (0.5 CO2 per amine). (c) CO2 adsorption isotherms obtained at 50 °C for e-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc), nPr-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc), iPr-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc), and cy-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc). (d) CO2 adsorption isotherms obtained at 75 °C for nBu-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc) and iPent-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc). All isotherm samples were activated under flowing N2 at the previously described temperatures (Table S2) for 0.5 h, followed by activation under high vacuum (<10 μbar) at 110 °C for 4 h. (e) Single-component gas adsorption isotherms for e-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc) at 30 °C. Closed and open circles represent adsorption and desorption data, respectively. A capacity of 2 mmol/g corresponds to 1 CO2 adsorbed per 2 molecules of e-2-OH.
