Figure 7.
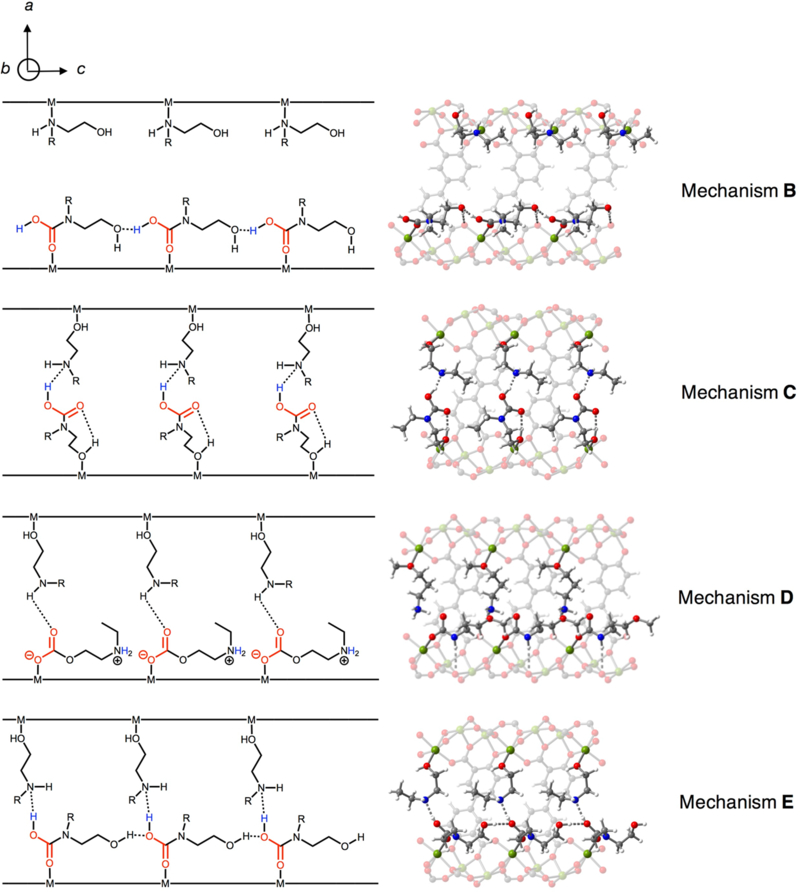
Additional mechanisms considered for CO2 adsorption in e-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc), as viewed along the c-axis (according to Figure 1 reference axes). Grey, red, blue, white, and green spheres represent C, O, N, H, and Mg atoms, respectively. Mechanism B features a single carbamic acid chain and free alcoholamine across the a-b plane without stabilizing hydrogen bonding interactions as present in mechanism A. Mechanism C features dangling carbamic acids stabilized by the free amines across the pore that are capable of hydrogen bonding interactions. In this mechanism, no interactions are present along the c-axis of the framework. Mechanism D features a single ammonium alkylcarbonate chain with hydrogen bonding stabilization in the a-b plane by an adjacent amine. Mechanism E features a carbamic acid chain with stabilization in the a-b plane, but with the uninserted alcoholamine in the “opposite” configuration to that in mechanism A.
