Figure 9.
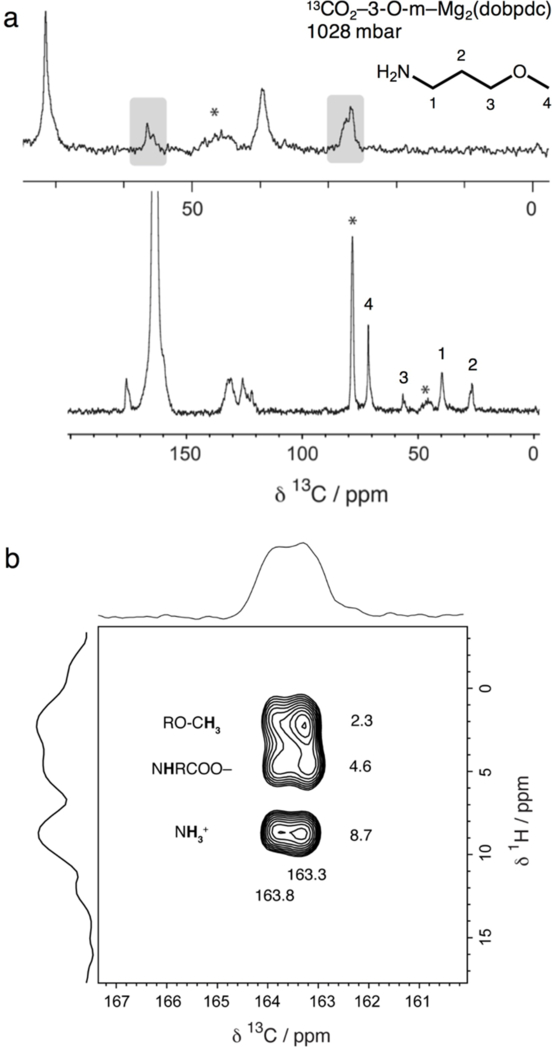
(a) 13C cross polarization (contact time 1 ms) NMR spectrum of 13CO2-dosed 3-O-m–Mg2(dobpdc). The split alkyl resonances are roughly equivalent (grey boxes). The carbonyl carbon chemical shift (163.6 ppm) is larger than that of e-2-OH–Mg2(dobpdc), likely due to formation of an ammonium carbamate species. Asterisks mark spinning sidebands. Minor peaks within the 120–180 ppm region correspond to the dobpdc4− linker. (b) 13C–1H HETCOR (contact time 100 μs) NMR spectrum for 13CO2-dosed 3-O-m–Mg2(dobpdc). Three dominant correlations are observed at 1H shifts of 2.3, 4.6, and 8.7 ppm (assigned to the methyl ether protons, inserted amine proton, and ammonium group of an ammonium carbamate, respectively) and 13C shifts of 163.3 and 163.8 ppm. The two sets of correlations observed in the 13C dimension suggest the presence of two subtly different local carbonyl environments.
