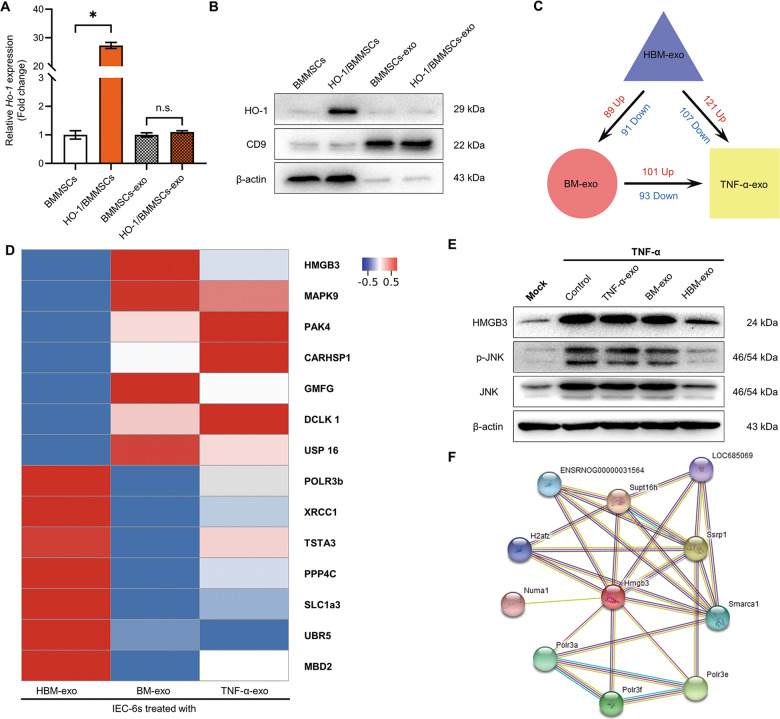
Fig. 4. HBM-exo downregulated the intracellular HMGB3/JNK pathway.
a, b QRT-PCR and western blotting were used to detect the expression levels of Ho-1 mRNA (a, fold change relative to cells or exosomes of BMMSCs, n = 3) and HO-1 protein (b) of HO-1 in BMMSCs and HO-1/BMMSCs cells and exosomes. c, d Proteomic analysis of the effect of HBM-exo on inflammatory stimulation. The HBM-exo treatment group, BM-exo treatment group, and TNF-α-exo treatment group were compared; the number of DAPs (c) and the DAPs (d) among the three groups is shown using a Heatmap. e The intracellular HMGB3, phosphorylated (p-) JNK, and JNK protein of the Mock group, TNF-α group, and TNF-α-exo, BM-exo, and HBM-exo groups was detected using western blotting. f The proteins interacting with HMGB3 were searched in the String database. *P < 0.05; ns no statistic, P > 0.05. BMMSCs bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; BM-exo BMMSCs co-culture system exosomes; CD9 CD9 molecule; DAPs differentially abundant proteins; Exo exosomes; HMGB3, high mobility group box 3; HO-1 heme oxygenase-1; HBM-exo HO-1/BMMSCs co-culture system exosomes; IECs intestinal epithelial cells; JNK C-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; qRT-PCR quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; TNF-α tumor necrosis factor alpha; TNF-α-exo tumor necrosis factor alpha-treated IEC-6s system exosomes.