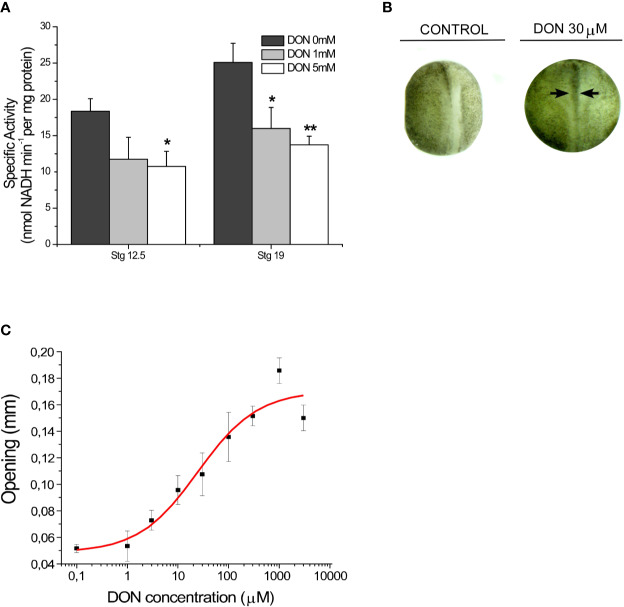
Figure 2.
GLS1 inhibition results in a NTDs phenotype in Xenopus laevis embryos. (A) Inhibition of enzymatic activity of GLS1 using DON in embryo samples at stage 12.5 and stage 19. GLS1 activity is significantly reduced with DON concentrations of 1 and 5 mM (n = 6). DON inhibition in kidney samples was also performed (Supplementary Figure S1). (B) Sample phenotypes obtained at stg 20 after DON incubation during neurulation, using 0 and 30 µM of DON. Controls were established using a 10% MMR saline solution. After incubation embryos were washed and placed in a 10% MMR saline solution. (n = 6) (C) NTDs severity was measured by examining the horizontal opening of the neural tube (black arrows from B) after incubation with different concentrations of DON (1 µM, 3 µM, 10 µM, 30 µM, 100 µM, 300 µM, 1 mM, 3 mM, and 10 mM). Controls were established using a 10% MMR saline solution. The maximal severity was obtained with 1mM of DON (0.18 mm opening) (n = 6; EC50 of 25 ± 15 µM). (Results expressed as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.