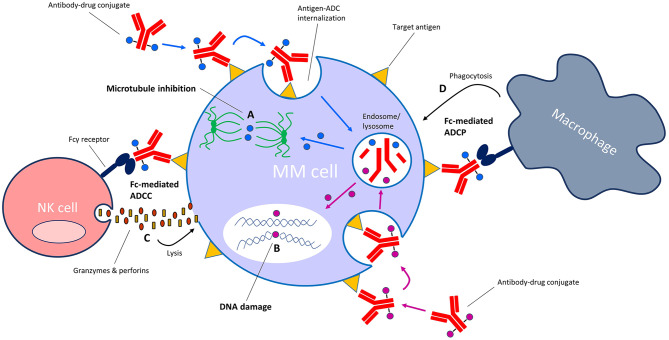
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) with microtubule-inhibiting or DNA-damaging payloads. Following binding of the ADC to its specific target on the cell surface, the antigen-ADC complex is internalized into the cell and the cytotoxic payload is released from the endosome/lysosome into the cytosol. Depending on the type of payload, the payload then either (A) inhibits microtubule formation or (B) induces damage to cellular DNA (e.g., strand breaks, alkylation). ADCs with an intact Fc tail may also induce Fc-mediated effector functions such as (C) antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and/or (D) antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).