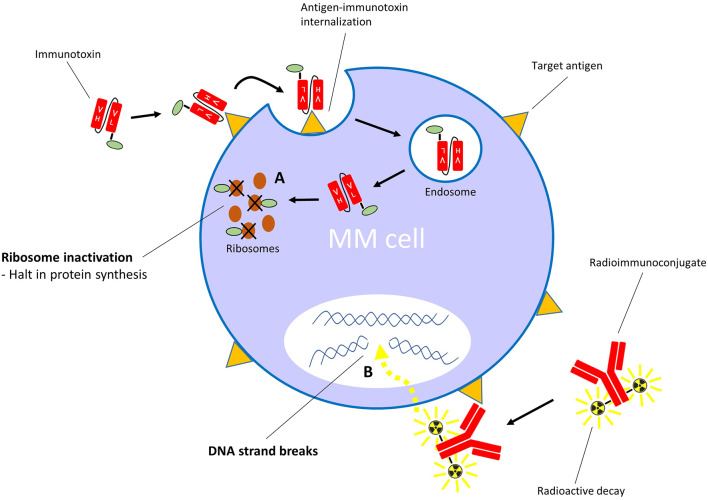
Figure 3.
Mechanism of action of immunotoxins with ribosome-inactivating toxins, and radioimmunoconjugates. (A) After binding its specific cell surface target, the immunotoxin is internalized into the cell. The toxin moiety then inactivates ribosomes, which leads to inhibition of polypeptide chain elongation. (B) The radioimmunoconjugate binds its specific target on the cell surface. Irradiation of cells within the path length of the emitting radionuclide results in DNA strand breaks.