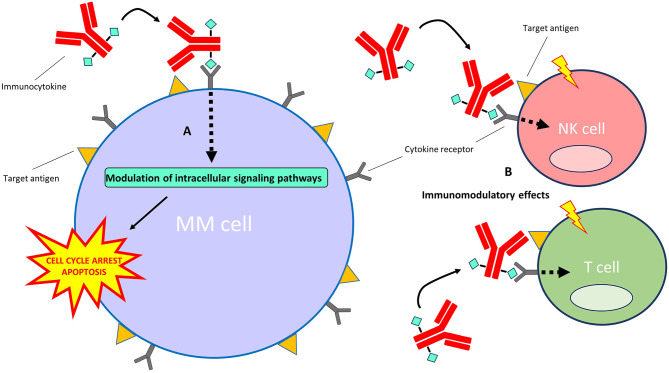
Figure 4.
Mechanism of action of immunocytokines. After the immunocytokine binds to its specific target on the cell surface, the cytokine moiety is able to signal via its native cytokine receptor. (A) Direct effects on MM cells: the modulation of intracellular signaling pathways by certain cytokines (e.g., interferon-alpha and TRAIL) induces cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis of MM cells. (B) Indirect effects on immune cells: modulation of intracellular signaling pathways by certain cytokines (e.g., interferon-alpha and interleukin-2) results in the stimulation of immune cell subsets, including T cells, NK cells, monocytes/macrophages (not depicted) and dendritic cells (not depicted), in the tumor microenvironment.