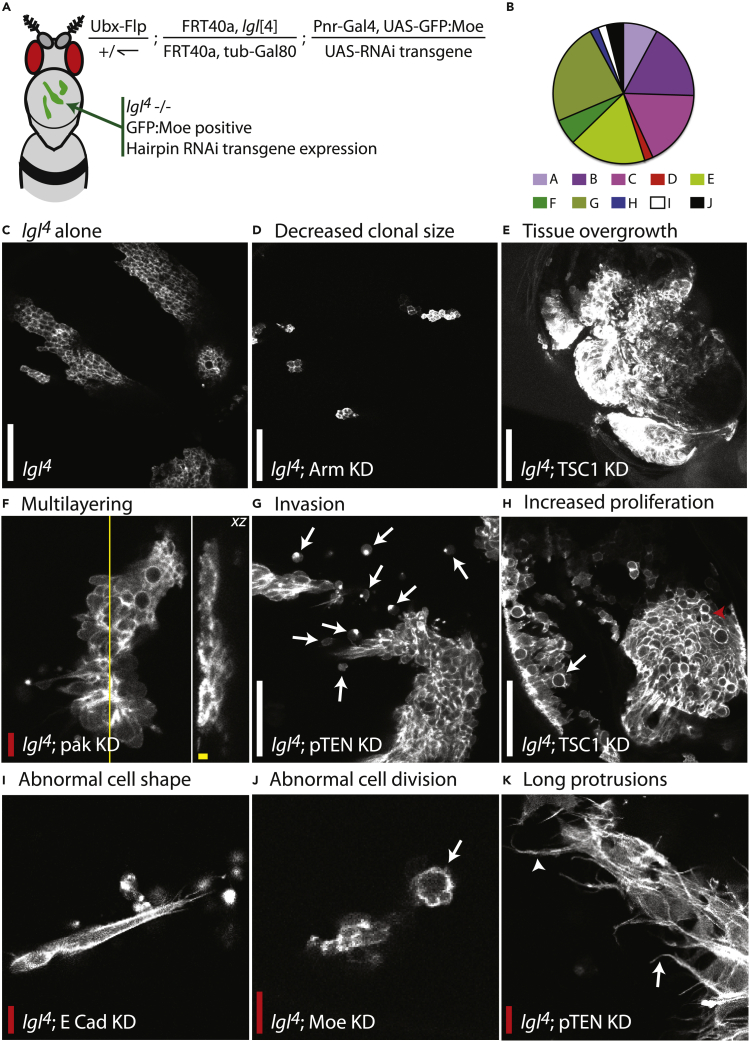
Figure 2.
Pilot Screen Identifies Several Modulators of Tumor Behavior
(A) Schematic illustrating how clones with distinct genotypes were generated on the back of the fly. The MARCM system was employed to generate mutant clones specifically within the fly dorsal thorax, through the use of Ubx-Flp. This generated GFP:Moe-labeled lgl4 homozygous mutant clones. RNAi transgene expression, and therefore gene KD, was restricted to the labeled lgl4 mutant tissue.
(B) Pie chart illustrating the range of biological functions from those genes included in the pilot screen. (A) apicobasal polarity, (B) cell adhesion, (C) cytoskeleton, (D) axon guidance, (E) cell cycle, (F) gene expression, (G) signaling, (H) mitochondria, (I) others, (J) unknown.
(C–K) Examples of phenotypes observed within the pilot screen. In the pilot screen we observed effects on clonal size (D and E), tissue morphology (E and F), cell morphology (I and K), and cell behavior (G, H, and J). These are just a few examples of the many distinct phenotypes that we observed. Panel (C) shows lgl4 clones for comparison. Arrows: (G) invading cells, (H) dividing cells, (J) a blebbing dividing cell, and (K) very long basal protrusions. Arrowheads: (H) cell doublet following cytokinesis and (K) long protrusions joining to form a fascicle. White scale bar, 50 μm; red scale bar, 10 μm; yellow scale bar, 10 μm in xz plane.