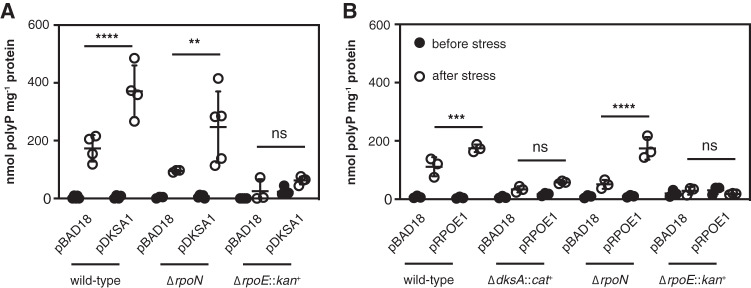
FIG 7.
Complementation of polyP-deficient mutants with ectopically expressed DksA and RpoE. E. coli MG1655 wild-type and isogenic ΔdksA1000::cat+, ΔrpoN730, or ΔrpoE1000::kan+ strains containing pBAD18 or the indicated pBAD18-derived plasmids were grown at 37°C to an A600 of 0.2 to 0.4 in rich medium (LB) containing 100 μg · ml−1 ampicillin (black circles) and 0.2% (A) or 0.0125% (B) arabinose and then shifted to minimal medium (MOPS with no amino acids, 4 g · liter−1 glucose, 0.1 mM K2HPO4, and 0.1 mM uracil) containing 100 μg · ml−1 ampicillin and 0.2% (A) or 0.0125% (B) arabinose for 2 h (white circles) (n = 3 to 5, ±SD). Growth medium for rpoE mutants included 10 μg · ml−1 erythromycin in both rich and minimal media. polyP concentrations are in terms of individual phosphate monomers. Unless specifically indicated, asterisks indicate polyP levels significantly different from those of the wild-type control for each experiment (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA or mixed-effects model with Holm-Sidak multiple-comparison test; ns, P > 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001).