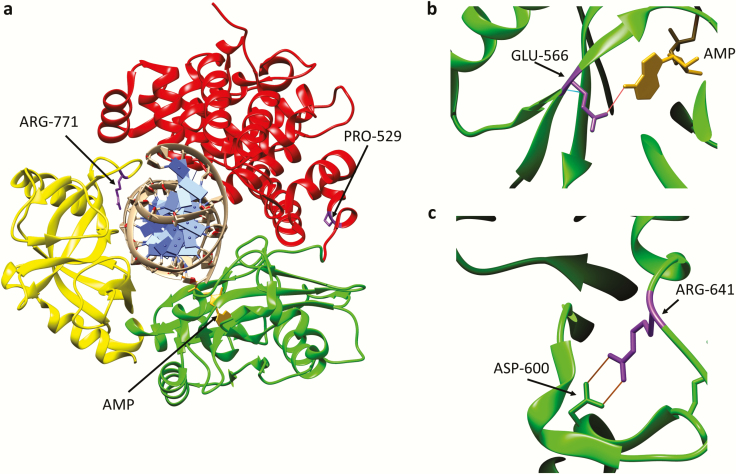
Fig. 3.
Amino acid substitutions identified in individuals with DNA ligase I deficiency syndrome. (a) Ribbon diagram showing the Adenylation domain (AdD, green), OB-fold domain (OBD, yellow) and DNA binding domain (DBD, red) of DNA ligase I encircling a nicked DNA duplex (grey). The AMP group (gold) linked to the 5-phosphate terminus of the DNA nick held within the AdD is indicated. Substitution of Arg771 (purple) in the OBD alters interaction with DNA, resulting in reduced enzymatic activity. with Trp and Pro529 depicted in purple. Substitution of Pro529 (purple) in the DBD with Leu has no effect on enzymatic activity. (b) Glu566 residue (purple) forms a hydrogen bond with N6 of the AMP moiety (gold). Replacement of Glu566 Lys inactivates enzyme activity. (c) Arg641 (purple) forms a salt bridge with Asp600 within the AdD domain. Replacement of R641 with Leu disrupts the salt bridge, resulting in reduced enzymatic activity that appears to be due to defective DNA binding.