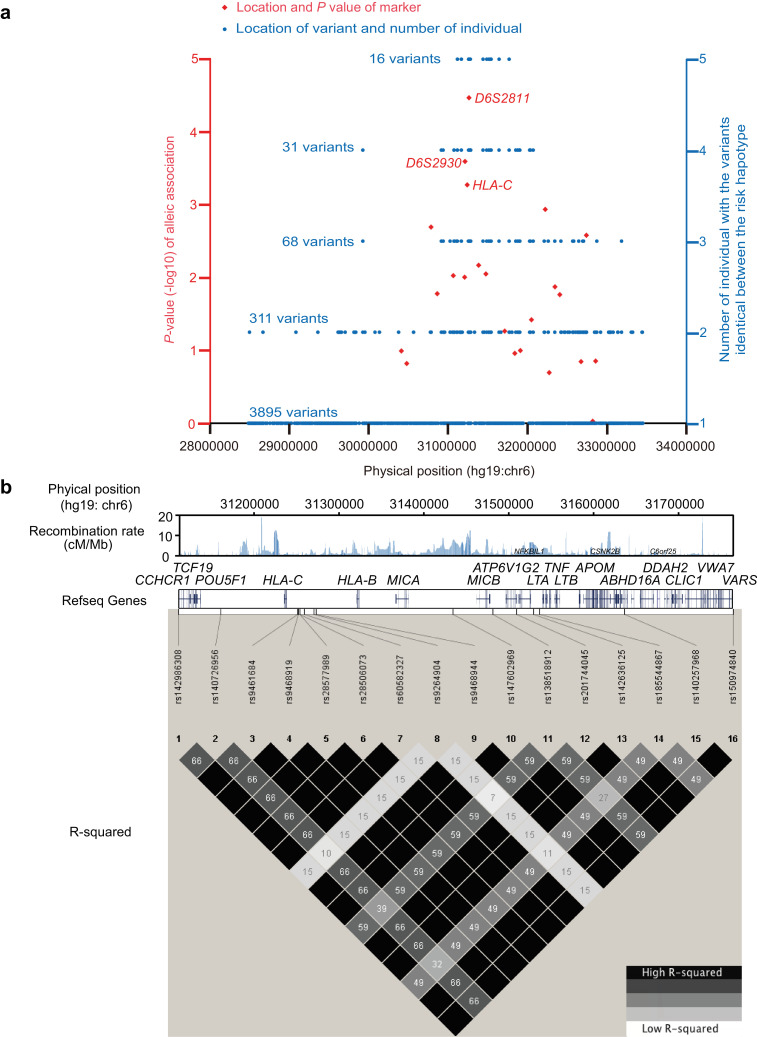
Fig. 1.
Identification of AA susceptibility gene within the MHC region by haplotype sequencing. (a) Association analysis and risk haplotype resequencing of the MHC region. Red diamonds indicate P values (-log10 scale) and locations. Three diamonds refer to haplotypes used for downstream analysis. Blue circles indicate individuals with variants identical between risk haplotype cases and the variant locations. (b) Pair-wise LD between 16 variants identified by NGS using genotype data from89 Japanese individuals obtained with the 1000 Genomes Browser. Upper track shows recombination rate (cM/Mb) estimated from Phase II HapMap data (release 21), middle track the gene map (RefSeq genes) generated with the UCSC Genome Browser, and lower track the pair-wise LD between the 16 variants in R-squared. (c) EHH analysis of core alleles at 43 loci displaying LD with the T allele of rs142986308. An estimated 43 loci haplotypes encompassing 24 SNVs of CCHCR1 and 19 multi-allelic loci (2.32Mbp) were used for this investigation. The 7 selected core alleles were as follows:rs142986308 allele T, rs142986308 allele C for the internal control, 4 SNVs that displayed LD with rs142986308 (Supplementary Fig. 28), and HLA-C*04:01 (Supplementary Fig. 3) as functional variants. (d) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of CCHCR1 showing evolutionarily conserved amino acids. The sequences, except for Hap01 and Hap26, were NP_001009009 (Pan troglodytes), NP_001108422 (Macaca mulatta), XP_532,064(Canis lupus familiaris), NP_001019707 (Bos taurus), NP_666,360 (Mus musculus), and NP_001116918 (Xenopus tropicalis). Blue indicates residues that prefer to form coiled-coil domains (Ala, Glu, Lys, Leu, Arg) and red indicates aromatic residues that do not prefer to form coiled-coil domains. Arrow and box indicate the position of substitution of p.Arg587Trp (rs142986308). (e) Coiled-coil structure prediction of CCHCR1 in the AA-associated haplotype and different species using COILS v2.2. The Y axis indicates the probability of coiled-coil conformation and the X axis amino acid residue number. Full amino acid sequences are described in Supplementary notes. Multiple amino acid sequence alignments were assigned to the probabilities of coiled-coil conformation for each haplotype and specie. Line brakes correspond to gaps in the multiple alignments. Arrow shows position of p.Arg587Trp (rs142986308).