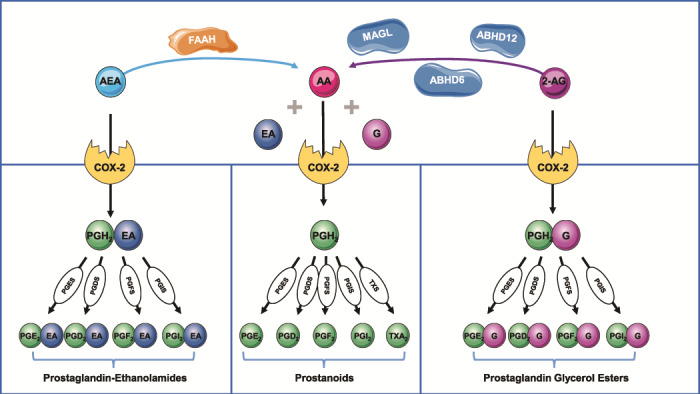
Figure 3. Crosstalk between the endocannabinoid and eicosanoid system pathways. FAAH is the main enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of AEA into arachidonic acid (AA) and ethanolamine (EA). 2-AG is mainly degraded by MAGL and, to a smaller extent, by ABHD6 and ABHD12 into AA and glycerol (G). AA is metabolised by cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) leading to the formation of the endoperoxide PGH2. Tissue specific metabolism of PGH2 by PG synthases (PGS) yields the different prostanoids: prostaglandins (PGD2, PGE2 and PGF2α), prostacyclin (PGI2) and thromboxane A2 (TXA2). AEA and 2-AG are also metabolised by COX-2 to produce prostaglandins–ethanolamides (or prostamides) and prostaglandin glycerol esters, respectively. However, as yet the molecular targets of these lipid mediators have not been totally elucidated. This image contains some elements adapted from the Servier Medical Art Image Bank (Servier Laboratories (Aust) Pty Ltd) licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.