Figure 2.
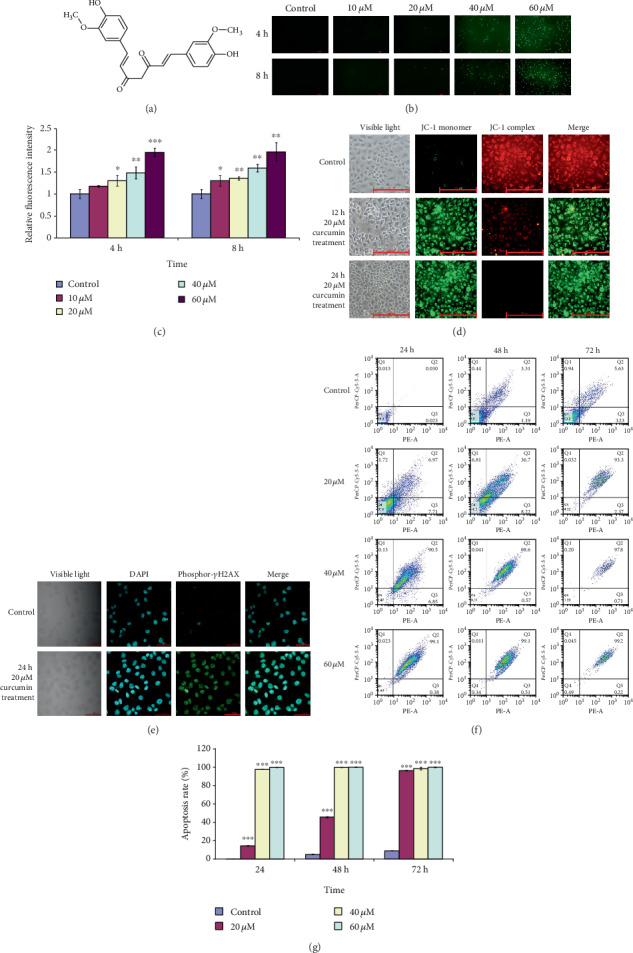
Curcumin elevates ROS levels and triggers mitochondrial damage, DNA damage, and apoptosis of hGCCs. After hGCCs were treated with different concentrations of curcumin for 24, 48, and 72 h, ROS levels, mitochondrial damage, nuclear DNA damage, and apoptosis were assayed. (a) The structure of curcumin. (b) The level of ROS was determined by a fluorescent dye of DCFH-DA, and (c) the fluorescence intensity (EX/EM = 485/535 nm) of DCFH-DA was measured. (d) The mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) was determined by a fluorescence probe of JC-1. (e) DNA damage was determined by immunocytochemistry of phosphor-γH2AX (Ser139). (f) Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry, and (g) the apoptosis rate (%) was calculated as follows: (the number of apoptotic cells/the number of detected cells) × 100%. All experiments were carried out in triplicate, and the data are shown as the mean ± SD. The single factor variance analysis was used to compare the significance between groups: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Difference with p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
