Figure 1.
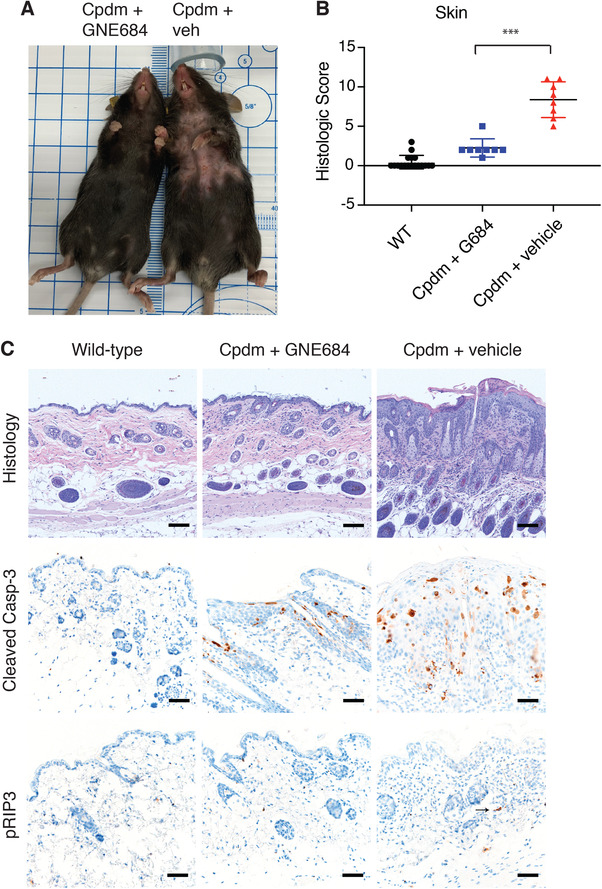
RIP1 kinase inhibition resolves dermatitis in Cpdm mice. (A) resolution of dermatitis and alopecia is observed in the Cpdm mouse treated with GNE684 (left) compared to the vehicle treated Cpdm mouse (right). (B) Histologic scores of dermatitis in wild‐type (N = 18), GNE684 treated Cpdm (N = 8), and vehicle treated Cpdm (N = 8) mice. Asterisks indicate P = 0.0003. Bar depicts mean with sd, P‐value was determined by Mann‐Whitney test. (C) Representative H&E stained, and cleaved caspase‐3 and phospho RIP3 (pRIP3) immunolabeled sections of mice from (B) demonstrating decreased dermal infiltrates, epidermal hyperplasia crusting, or ulceration, and decreased cleaved caspase‐3 and RIP3 phosphorylation in Cpdm mice following treatment with GNE684. The arrow indicates a pRIP3 positive cell
