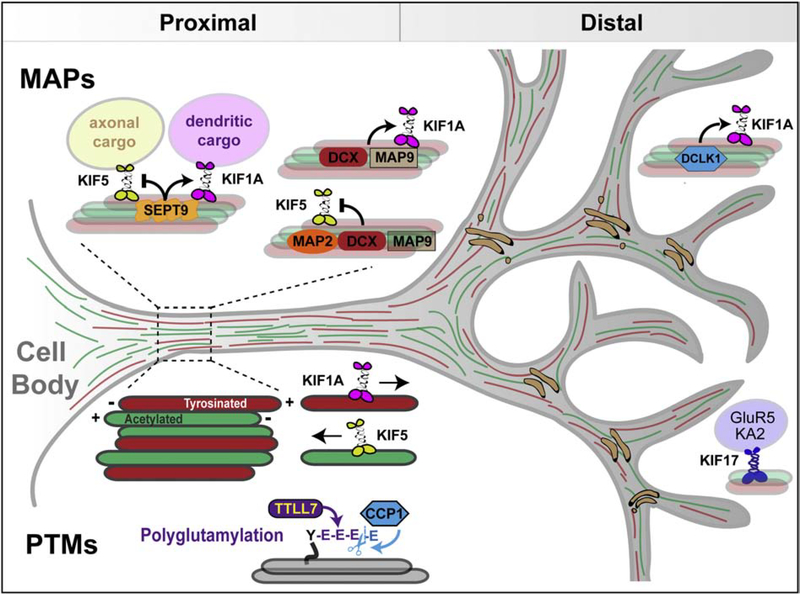
Figure 4.
Spatial control of dendritic membrane traffic by MAPs and microtubule PTMs. Schematic depicts dendritic MAPs and microtubule PTMs with roles in the regulation of kinesin-driven membrane traffic. SEPT9 and DCLK1 localize in proximal and distal dendrites, respectively. SEPT9 impedes traffic of axonal cargo of kinesin-1 into dendrites, while it promotes the anterograde transport of dendritic cargo of kinesin-3. DCLK1, DCX and MAP9 also promote the microtubule binding and motility of kinesin-3. In vitro motility assays indicate that MAP2, DCX and MAP9 inhibit kinesin-1 motility, but it is unknown whether these MAPs can impede entry of kinesin-1 and its axonal cargo into dendrites. Dendrites contain tyrosinated and acetylated microtubules, which are oriented with their plus-ends away and toward the cell body, respectively. The kinesin-3/KIF1A motor associates preferentially with tyrosinated plus-end out microtubules and kinesin-1/KIF5 interacts with acetylated plus-end in microtubules. Dendritic microtubules are also modified with short glutamate chains, which are maintained by the tubulin glutamylase TTLL7 (tubulin tyrosine like ligase 7) and the deglutamylase CCP1 (cytosolic carboxypeptidase 1). Note that kinesin-2/KIF17 transports the kainate receptors GluR5 and KA2 in distal dendrites, which is indicative of a spatial specificity in dendritic motor-cargo traffic.