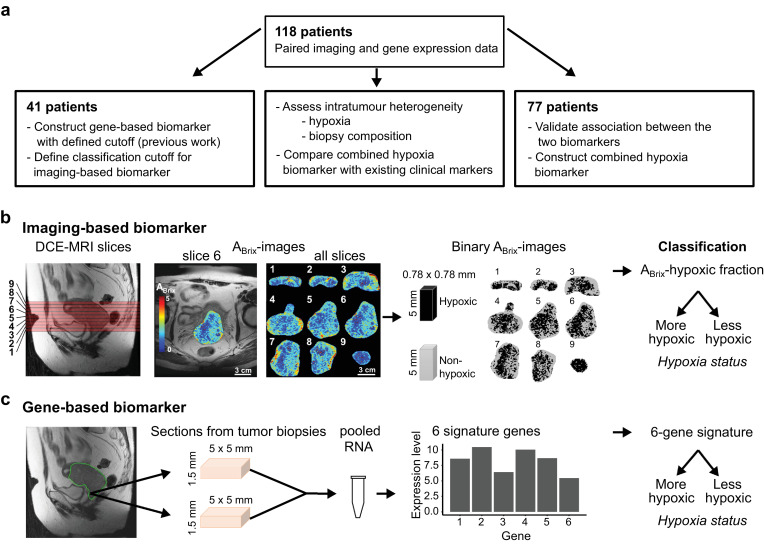
Fig. 1.
Study design and hypoxia biomarkers. (a) Patients included at different stages of the study. Independent subgroups of the total cohort of 118 patients were used to determine biomarker cutoff for classification (n = 41) and to validate the association between the biomarkers and construct the combined biomarker (n = 77). The total cohort was used to assess the importance of intratumour heterogenity for biomarker performance and compare the combined biomarker with existing clinical markers. (b) Determination of the imaging-based biomarker from left to right, sagittal T2W-image of the pelvic showing localization of image slices numbered from lower to upper part of the tumour, example of axial ABrix-image of the tumour (slice 6) superimposed on T2W-image, ABrix-images of all slices covering the tumour, binary ABrix-images of the same slices showing voxels in hypoxic and non-hypoxic regions according to an ABrix threshold value of 1.56, and classification based on the hypoxic fraction of all slices combined. (c) Determination of the gene-based biomarker from left to right, sagittal T2W-image of the pelvic showing localization of the region accessible for biopsies in the lower part of tumour, the approximate size of the sections from 1–4 biopsies (median 2) taken from each tumour and pooled for RNA isolation, expression data of 6 signature genes, and classification based on the signature value.