FIGURE 1.
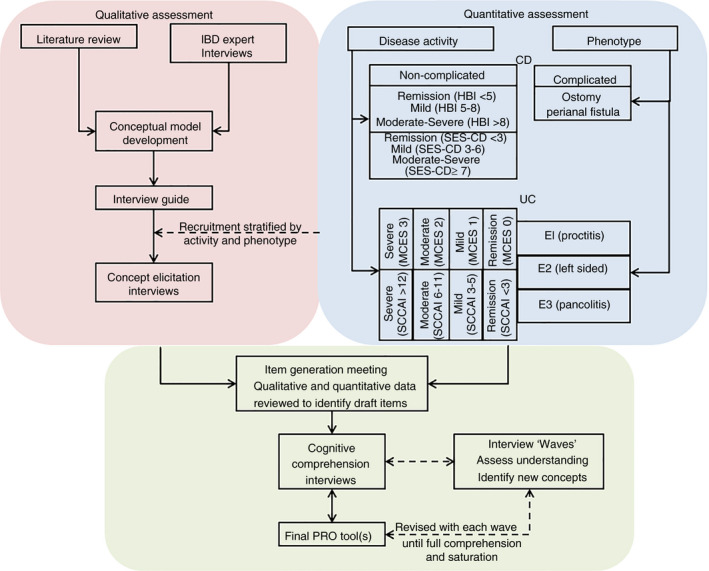
SIQ‐CD and SIQ‐UC development activities. We performed quantitative and qualitative assessments when building novel patient‐reported outcome (PRO) instruments for use in Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Disease activity and phenotype were evaluated during the screening process. CD patients were categorised as having “complicated” (ie an ostomy or perianal fistula) or “non‐complicated” disease. The Harvey Bradshaw Index (HBI) was used to quantify clinical disease activity. Participants without complications were required to undergo endoscopy at baseline, and a centrally read Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn's Disease (SES‐CD) was collected to characterise the study population. All UC participants underwent endoscopy at baseline, and centrally read Mayo Clinic Endoscopic Scores (MCES) were used to assess endoscopic disease activity. Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index (SCCAI) scores and disease extent were also collected to characterise the study population. Qualitative assessments included a literature review, interviews with key opinion leaders and concept elicitation interviews. Once the concept elicitation interview results were analysed, an item generation meeting took place to review draft PRO items. The draft CD and UC instruments were piloted in waves of cognitive comprehension interviews to assess patient understanding and feasibility. Revisions to the draft instruments were made based on the cognitive compression interview results
