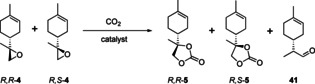
Table 9.
Reaction of 4 with CO2.[a]
|
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Entry |
Catalyst |
T [°C] |
p [bar][b] |
t [h] |
R,S/R,R 4 after reaction |
Conv. [%][c] |
Chemoselectivity 5 [%] |
R,S/R,R 5[ d] |
|
1 |
[Bu4N]Br (3) |
140 |
75 |
2.5 |
54:46 |
80 |
96 |
70:30 |
|
2 |
[Bu4N]Br (3) |
120 |
75 |
4.5 |
58:42 |
76 |
91 |
65:35 |
|
3 |
[Bu4N]Br (3) |
120 |
75 |
2.5 |
59:41 |
52 |
99 |
67:33 |
|
4 |
[Bu4N]Br (3)+A (2) |
120 |
75 |
2.5 |
64:36 |
68 |
98 |
73:27 |
|
5 |
A (2) |
120 |
75 |
2.5 |
64:36 |
46 |
86 |
83:17 |
|
6 |
[Bu4N]Br (3)+B (2) |
120 |
75 |
2.5 |
61:39 |
57 |
76 |
63:37 |
|
7 |
B (2) |
120 |
75 |
2.5 |
62:38 |
63[e] |
0[f] |
– |
|
8 |
B (2) |
120 |
– |
2.5 |
56:44 |
75[g] |
0[h] |
– |
|
9 |
no catalyst |
120 |
75 |
2.5 |
63:37 |
–[i] |
– |
– |
[a] Reaction conditions: 4 (2.3 mmol) (initial ratio of 63:37 R,S/R,R), biphenyl (10 mol %) as an internal standard, stirrer speed 300 rpm. [b] Pressure of CO2 at 40 °C. [c] Determined from quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy. [d] From 1H NMR using doublet at 4.25 ppm, overlapping doublets were deconvoluted using MNova. [e] Up to 63 % depending on the batch of B. [f] Reaction yields 41 with 50 % selectivity. [g] Up to 75 % depending on the batch of B. [h] Reaction yields 41 with 47 % selectivity. [i] 6.5 % mass loss.