Figure 2.
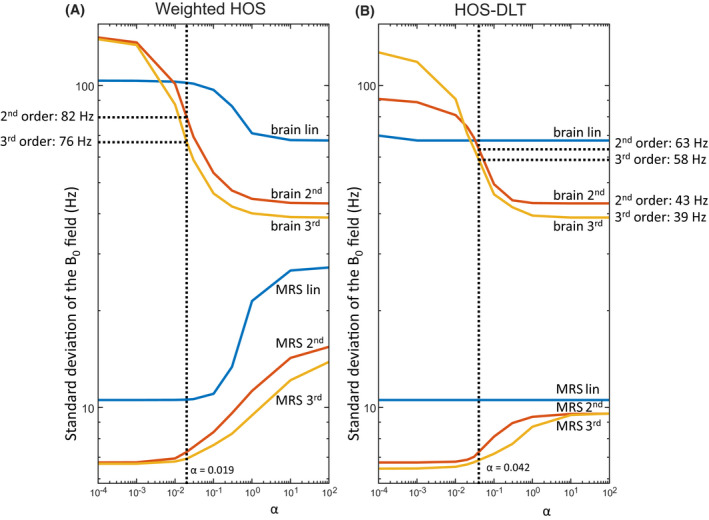
Analysis of the cost function weight for a single voxel MRS shim volume of interest (VOI) in the hippocampus in a single subject. Results for different shim orders are plotted on a double logarithmic scale as standard deviation over the respective shim VOI. With weighted static higher order shimming (A, wHOS), the α dependent trade‐off between brain and voxel homogeneity can be seen from the low standard deviation of the field with higher α (top three lines; blue for linear, red for second order and yellow for third order shimming) and the low standard deviation of the field in the voxel with low α (bottom three lines). At a cut‐off of 0.5 Hz above optimal MRS‐voxel shim for third order shimming at α = 0.019, the whole brain standard deviation reached 82 Hz and 76 Hz for second and third order respectively. Using weighted static higher order shimming with dynamic linear terms (B, HOS‐DLT), a higher α could be used (α = 0.042) to achieve a better whole brain homogeneity at similar MRS homogeneity. For linear shimming, optimal shimming was possible in all cases, for second order shimming 63 Hz and for third order shimming 58 Hz was reached. This is still above the optimal 43 Hz and 39 Hz that was reached with a whole brain optimization (or using a high alpha value) using second and third order shim order respectively
