Figure 5.
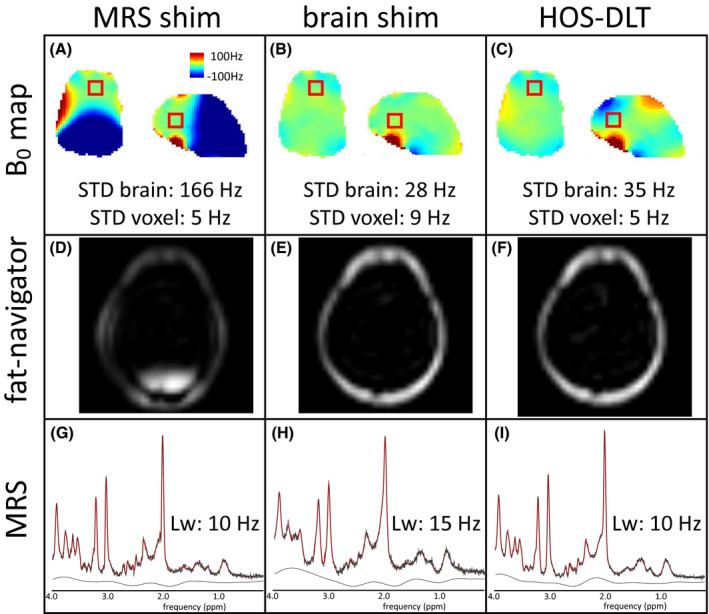
The B0 shim results (A‐C) in a single subject show the trade‐off between the optimization approaches for fat‐navigator interleaved MRS, with the fat‐navigator results shown in D‐F and the MRS results in G‐I. First, for the optimization on only the MRS shim volume of interest (VOI) (left column) we see a good homogeneity in the MRS voxel but high frequency offsets outside the MRS voxel (A). This compromises the fat‐selectivity of the navigator in the back of the head (D) but leads to good spectral resolution of 10 Hz (G). Second, a shim optimization on only the brain shim VOI (middle column) shows a good global homogeneity (B), resulting in good fat‐selectivity (E) but in reduced spectral resolution in MRS of 15 Hz (H). With the combined optimization using the HOS‐DLT shim (right column), both good global homogeneity was achieved (C, showing the HOS‐DLT map for the brain VOI shim) that allows for good fat‐selectivity (F) and good spectral resolution at 10 Hz was achieved (I)
