Figure 2.
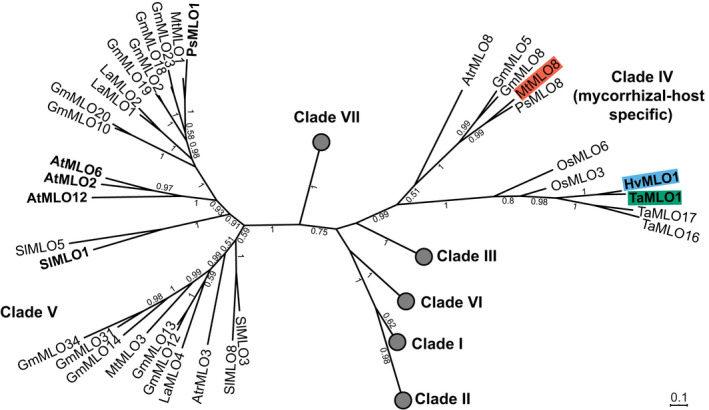
MLO phylogeny. A phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between MLO proteins from Amborella trichopoda (Atr), Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Beta vulgaris (Bv), Dianthus caryophyllus (Dc), Glycine max (Gm), Hordeum vulgare (Hv), Lupinus angustifolius (La), Medicago truncatula (Mt), Oryza sativa (Os), Pisum sativum (Ps), Physcomitrella patens (Pp), Solanum lycopersicum (Sl) and Triticum aestivum (Ta). The T. aestivum MLO protein dataset often included near‐identical homoeoalleles (A, B and D copies); therefore, for simplicity, only one homoeoallele was included in the phylogenetic analysis (A homoeoallele where possible). The tree was generated using Mega X from an amino acid alignment. The phylogenetic tree was calculated via the maximum likelihood method, using Jones–Taylor–Thornton modelling with 100 bootstrap replications. Bootstrap values > 0.5 are shown. The scale bar indicates the evolutionary distance based on the amino acid substitution rate. Circles indicate collapsed clades; known powdery mildew susceptibility factors are labelled in bold, and candidate MLO proteins for a role in mycorrhization are highlighted.
