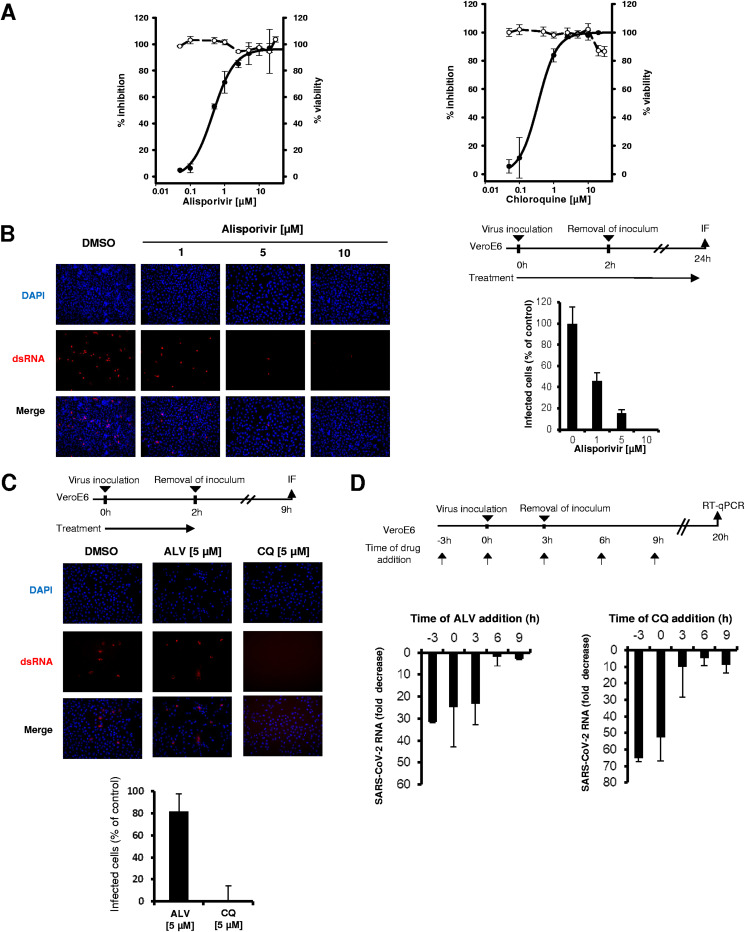
FIG 1.
Antiviral activity of alisporivir against SARS-CoV-2. The means ± standard deviations from 2 experiments performed in triplicate are shown. (A) Vero E6 cells were infected for 2 h with a SARS-CoV-2 clinical isolate at an MOI of 0.02 in the presence of increasing concentrations of alisporivir (left) or chloroquine (right). Cells were incubated for 48 h in the presence of the compounds, and SARS-CoV-2 RNA was quantified in cell supernatants by RT-qPCR (solid lines). Cell viability is shown with dashed lines. (B) SARS-CoV-2 infection of Vero E6 cells at an MOI of 0.4 assessed by immunofluorescence using anti-dsRNA antibodies in the presence of increasing concentrations of alisporivir. Infected cells were quantified using ImageJ software. (C) Effect of 5 μM alisporivir and 5 μM chloroquine on SARS-CoV-2 entry into Vero E6 cells, assessed by immunofluorescence using anti-dsRNA antibodies. (D) Time-of-addition experiments with alisporivir and chloroquine. Vero E6 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 at an MOI of 0.05 for 3 h; 10 μM alisporivir or 10 μM chloroquine was added at different time points and maintained until 20 h postinfection. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was quantified in cell supernatants by RT-qPCR. ALV, alisporivir; CQ, chloroquine.