Figure 1.
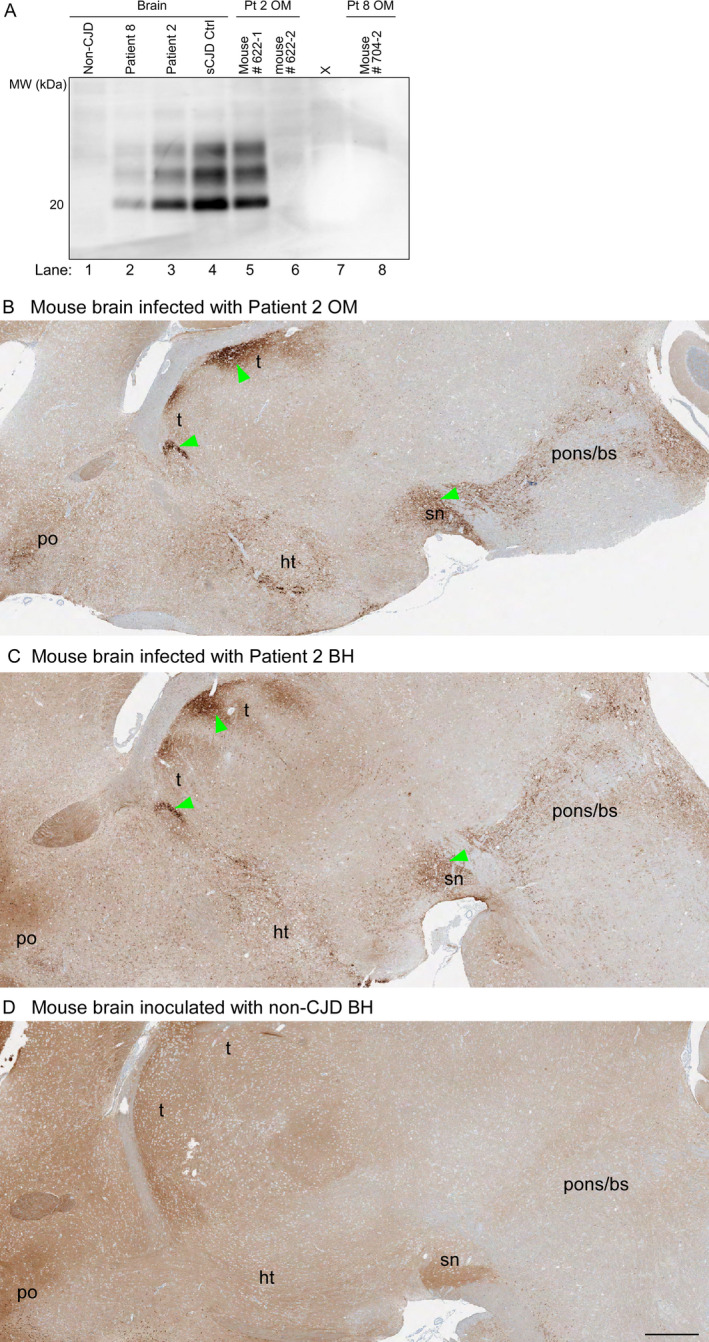
PrP analyses of inocula and brains from Tg66 mouse recipients. A, Immunoblots of PrPres in sCJD human brain inocula and brains of Tg66 mice inoculated with human brain or OM samples. Lanes 1–4: human brain homogenates from a non‐CJD control case and three MM1 sCJD cases (Patient 8, Patient 2, and a previously established positive control case (sCJD Ctrl). Lanes 5–6, 8: Tg66 mouse brain homogenates from individual animals inoculated with OM specimens from sCJD Patients 2 or 8 (Pt 2 and 8, respectively). Lane 7 contained an irrelevant sample. The position of a 20‐kDa molecular weight marker is shown on the left. B‐D, PrP immunohistochemical staining of brain sections from clinically affected Tg66 mice inoculated with OM (B) or brain homogenate (BH) (C) samples from sCJD Patient 2 (B, C) or a healthy mouse inoculated with healthy human (non‐prion disease) control BH (D). Brain regions: t = thalamus; po = preoptic area; ht = hypothalamus; sn = substantia nigra; pons/bs = pons/brain stem. B shows the single mouse that had clinical signs of prion disease following OM inoculation. Green arrows indicate examples of regions where abnormal PrP deposition was observed. Bar = 0.5 mm. PrP monoclonal antibody 3F4 was used as described in Methods
