Figure 3.
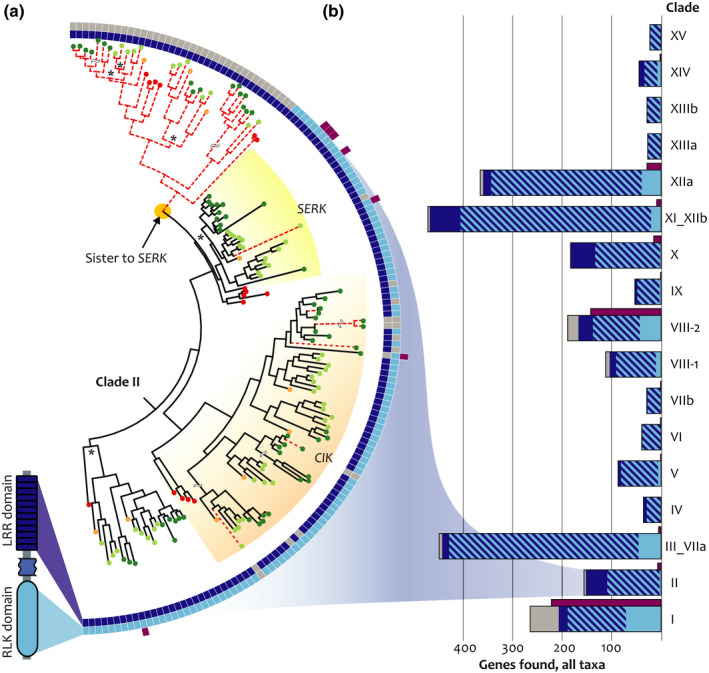
Structural modifications are common in the leucine‐rich repeat receptor‐like kinase (LRR‐RLK) family. (a) Clade II contains many structural variants. Squares on tree perimeter show the detected LRR (dark blue), RLK (light blue), and unrelated (purple) domains. A search using whole genes misses some members (dashed red lines), most notably a large clade of LRR‐only genes sister to the SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE (SERK) clade. All bootstrap support values < 70% marked with asterisk (see Supporting Information Fig. S2 for details). (b) Number of structural variants found in each clade (sum of nine species). Some clades are highly biased towards particular modifications, such as Clades II, X, and XI_XIIb (many LRR‐only genes) and Clades I, III_VIIa, VIII‐2, and XIIa (many RLK‐only genes). Purple bars depict the total number of genes with another domain type found, irrespective of LRR and RLK domain. Clades I and VIII‐2 have ancestral malectin‐like domains that are represented in purple bars.
