Figure 2.
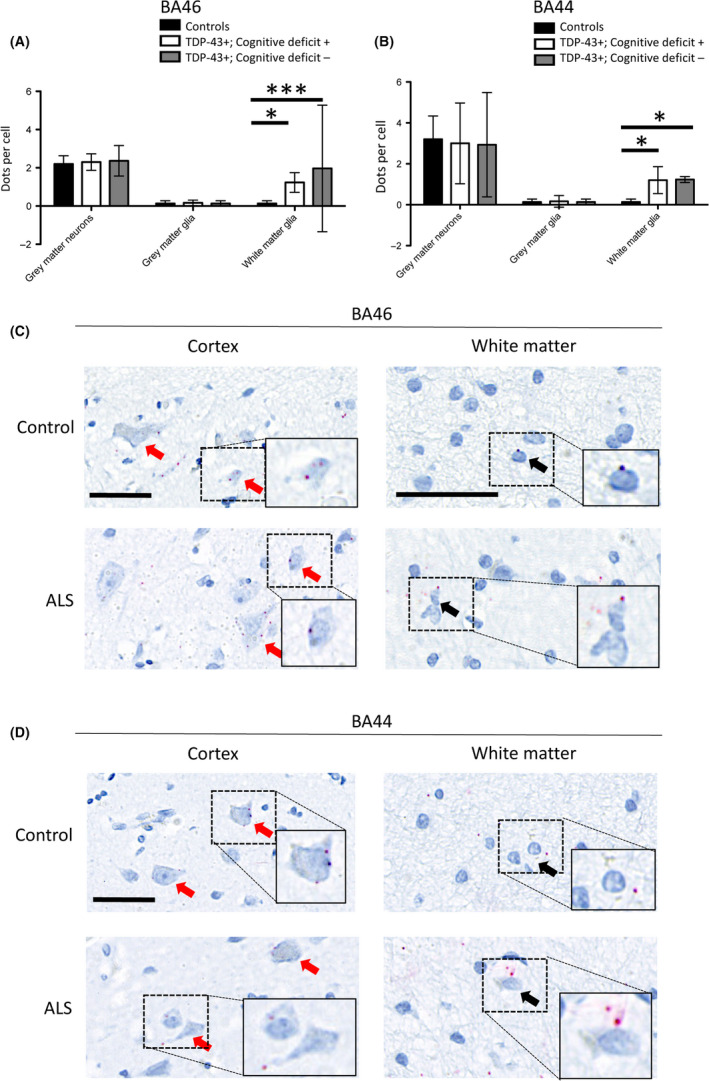
HspB8 expression is upregulated in the white matter glia of ALS patients compared to controls. (A) Graph quantifying grey matter neuronal and glial expression and white matter glial expression of HspB8, in the BA46 region associated with executive function, in cases with TDP‐43 pathology and cognitive deficits (TDP‐43+, Cognitive deficit+), mismatch cases (TDP‐43+, Cognitive deficit‐) and three non‐ALS/non‐neurological control cases (TDP‐43‐, Cognitive deficit‐); demonstrating upregulation of HspB8 in the white matter glia of all ALS cases exhibiting TDP‐43 pathology. ***Indicates P < 0.001, *Indicates P < 0.05, one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (n = 3 patients per group; 10 cells in each of 3 randomly selected high power fields of view were assessed per case). (B) Same as A but assessing the BA44 region associated with language and fluency. *Indicates P < 0.05, two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (n = 3 patients per group; 10 cells in each of 3 randomly selected high power fields of view were assessed per case). (C) Representative region of the brain associated with executive function (BA46), demonstrating neuronal (red arrows) and glial (black arrows) expression of HspB8, with increased HspB8 expression within white matter glia. Scale bars = 50 µm. (D) Representative region of the brain associated with language and fluency (BA44), demonstrating neuronal (red arrows) and glial (black arrows) expression of HspB8, with increased HspB8 expression within white matter glia. Scale bars = 50 µm.
