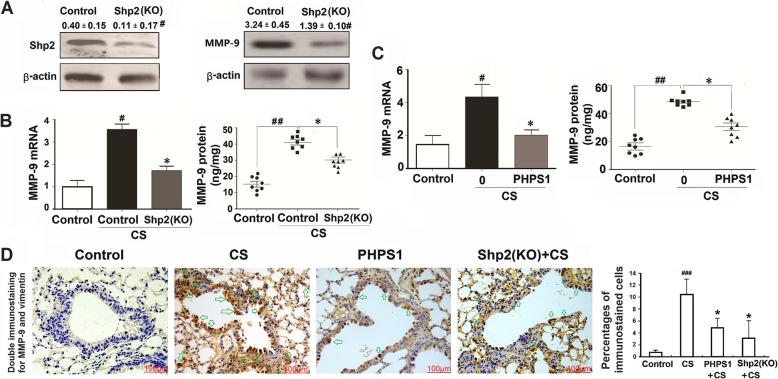
Fig. 2.
Genetic ablation of Shp2 in lung epithelial cells or pharmacological inhibition of Shp2 suppresses the CS-induced MMP-9 expression in mice. a Genetic ablation of Shp2 in lung epithelial cells significantly decreases Shp2 and MMP-9 protein expression in lung tissues. n = 8 per group, #p < 0.05 compared with control (WT mice). b Shp2 knockout in lung epithelial cells reversed the CS-induced MMP-9 mRNA and protein elevation in lung tissues. n = 8 per group, #p < 0.05 compared with control (WT mice), *p < 0.05 compared with control with CS (WT mice with CS exposure). c Shp2 inhibitor - PHPS1 (3 mg/kg, i.p daily injection) treatment reduces the CS-induced MMP-9 mRNA and protein elevation in lung tissues. N = 8 per group, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared with control (WT mice), *p < 0.05 compared with control with CS (WT mice with CS exposure). d Double immunostaining confirms Shp2 knockout in lung epithelial cells or us of the Shp2 inhibitor reduces the CS-induced the mesenchymal marker vimentin elevation in lung tissues. n = 8 per group, ##p < 0.01 compared with control (WT mice), *p < 0.05 compared with control with CS (WT mice with CS exposure). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Scale bar = 100 μm. Statistical significance is determined by one-way ANOVA followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test